MSDS Cryopreserved Cells
Instructions HDF
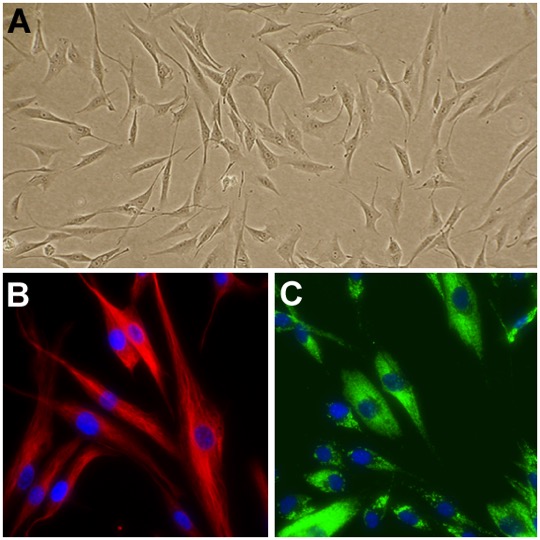
Cell Apps Flyer Skin Cells
5 Important Cell Culture Rules
Cell Apps Poster Primary Cells
Cell Applications Inc Brochure
Description
iPSC generation: HDF from Cell Applications have been instrumental to create and characterize induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), garnering a Nobel Prize for the technology in 2012.
Researchers have also employed our HDF to:
- Demonstrate the activation and efficiency of reprogramming, such as the transition of fibroblasts into platelets
- Identify markers that distinguish chondrocytes and synovial cells
- Establish protocols for tissue engineering, biomaterials, and synthetic collagens.
- Examine molecular gene regulation & activation, epigenetic modifications, histone ubiquitination and miRNA expression.
- Describe cell physiology and behavior, including cell adhesion, integrins, cartilage link protein and elastic fiber formation. Others rely on the cells to characterize mitochondrial metabolism, angiogenesis and tissue remodeling.
- Provide insights into disease and pathology: UVA effects, stress-induced premature senescence, skin aging, elasticity and dermal integrity, as well as tumor cell pluripotency markers.
- Develop potential clinical treatments and therapeutics: Cell survival factors and natural antioxidants like astaxanthin. Some investigators have observed approaches that promote wound healing, or protect skin from UVA-induced photo-aging.
Details
Tissue | Normal helathy human foreskin or adult skin |
QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma, virus |
Bioassay | Attach, spread, proliferate in Growth Med |
Cryovial | 500,000 HDF (primary culture) frozen in Basal Medium w/ 10% FBS, 10% DMSO |
Kit | Cryovial frozen HDF (106-05), Growth Medium (116-500), Subcltr Rgnt Kit (090K) |
Proliferating | Shipped in Gr Med, 1st psg (flasks or plates) |
Doublings | At least 15 |
Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Human Dermal Fibroblasts Total Kit, adult: 5x10^5 Cells (Adult), Medium & Subculture Reagents (See Details tab for specifics) | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: 106K-05a | Price: $442.00 | |
| Cryopreserved Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), adult: Frozen HDF (5x10^5) | Size: 1 Cryovial | CAT.#: 106-05a | Price: $275.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: T-25 Flask | CAT.#: 107-25a | Price: $275.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: T-75 Flask | CAT.#: 107-75a | Price: $465.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: 24 Well | CAT.#: 107-24Wa | Price: $465.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: 96 Well | CAT.#: 107-96Wa | Price: $585.00 | |
| Cryopreserved Human Dermal Fibroblasts Total Kit, neonatal: 5x10^5 Cells (Neonatal), Medium & Subculture Reagents (See Details tab for specifics) | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: 106K-05n | Price: $622.00 | |
| Cryopreserved Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), neonatal: Frozen HDF (5x10^5) | Size: 1 Cryovial | CAT.#: 106-05n | Price: $455.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), neonatal: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: T-25 Flask | CAT.#: 107-25n | Price: $455.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), neonatal: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: T-75 Flask | CAT.#: 107-75n | Price: $645.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), neonatal: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: 24 Well | CAT.#: 107-24Wn | Price: $645.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), neonatal: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: 96 Well | CAT.#: 107-96Wn | Price: $765.00 | |
| Cryopreserved Human Dermal Fibroblasts Total Kit, fetal: 5x10^5 Cells (Fetal), Medium & Subculture Reagents (See Details tab for specifics) | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: 106K-05f | Price: $662.00 | |
| Cryopreserved Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), fetal: Frozen HDF (5x10^5) | Size: 1 Cryovial | CAT.#: 106-05f | Price: $495.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), fetal: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: T-25 Flask | CAT.#: 107-25f | Price: $495.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), fetal: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: T-75 Flask | CAT.#: 107-75f | Price: $685.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), fetal: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: 24 Well | CAT.#: 107-24Wf | Price: $685.00 | |
| Proliferating Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), fetal: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: 96 Well | CAT.#: 107-96Wf | Price: $805.00 |
Related Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDF Growth Medium: All-in-one ready-to-use | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 116-500 | Price: $114.00 | |
| HDF Growth Medium Kit: Basal medium & growth supplement sold together packaged separately. | Size: Yields 500 ml | CAT.#: 116K-500 | Price: $136.00 | |
| HDF Basal Medium: Basal medium (contains no growth supplement). Add GS before use. | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 115-500 | Price: $74.00 | |
| HDF Growth Supplement: Added to Basal Medium to create Growth Medium. | Size: 15 ml | CAT.#: 116-GS | Price: $66.00 | |
| HDF Growth Medium, Xeno-free: All-in-one ready-to-use Xeno-Free for HDF | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 116XF-500 | Price: $137.00 |
Extended Family Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyclonal Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 Rabbit Antibody: Polyclonal Fibroblast Growth Factor 2, FGF2 (bFGF), Rabbit Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CA0259 | Price: $302.00 | |
| Polyclonal Fibroblast Growth Factor 7, KGF, Rabbit Antibody: Polyclonal Fibroblast Growth Factor 7, KGF, Rabbit Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CA0853 | Price: $302.00 | |
| Rabbit Fibroblast Growth Factor 8 Antibody: Rabbit Fibroblast Growth Factor 8 Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CA1216 | Price: $302.00 | |
| Mouse Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 Antibody: Mouse Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CP10102 | Price: $333.00 | |
| Polyclonal Fibroblast Growth Factor-Receptor 2 Antibody: Polyclonal Fibroblast Growth Factor-Receptor 2 Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CB4365 | Price: $333.00 | |
| Mouse Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 4 Antibody: Mouse Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 4 Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CP10103 | Price: $333.00 | |
| Rabbit Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Antibody: Rabbit Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CA1052 | Price: $302.00 | |
| Cyto-X Cell Counting Reagent: 500 tests | Size: 1 Bottle | CAT.#: 028-01 | Price: $160.00 | |
| Cyto-X Cell Counting Reagent Sample: 100 tests | Size: Sample | CAT.#: 028-S | Price: $41.00 | |
| Cytofect Fibroblast Transfection Kit (250 x 24-Wells): 250 x 24-Well Rxns | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: TF103K | Price: $465.00 | |
| Cytofect Fibroblast Transfection Sample Kit (25 x 24-Wells): 25 x 24-Well Rxns | Size: 1 Sample Kit | CAT.#: TF103KS | Price: $62.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 (FGF-21): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 | Size: 20 ug | CAT.#: RP1148-20 | Price: $194.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 (FGF-21): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1148-100 | Price: $484.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 (FGF-21): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1148-1000 | Price: $3,175.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-22 (FGF-22): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-22 | Size: 20 ug | CAT.#: RP1068-20 | Price: $194.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-22 (FGF-22): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-22 | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1068-100 | Price: $624.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-22 (FGF-22): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-22 | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1068-1000 | Price: $5,166.00 | |
| Human FGF9 ELISA Kit: Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 ELISA Kit | Size: 96 Wells | CAT.#: CL0348 | Price: $457.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-4 (FGF-4): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-4 | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: RP1031-25 | Price: $194.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-4 (FGF-4): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-4 | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1031-100 | Price: $484.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-4 (FGF-4): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-4 | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1031-1000 | Price: $3,175.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor Acidic (FGF-1): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-acidic | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: RP1029-10 | Price: $81.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor Acidic (FGF-1): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-acidic | Size: 50 ug | CAT.#: RP1029-50 | Price: $194.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor Acidic (FGF-1): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-acidic | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1029-1000 | Price: $1,561.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 147 Basic (FGF-147 basic/FGF-2): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-147-basic | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: RP1028-10 | Price: $81.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 147 Basic (FGF-147 basic/FGF-2): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-147-basic | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1028-100 | Price: $317.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 147 Basic (FGF-147 basic/FGF-2): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-147-basic | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1028-1000 | Price: $1,561.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 154 Basic (FGF-basic 154 / FGF-2): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-154-basic | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: RP1146-10 | Price: $81.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 154 Basic (FGF-basic 154 / FGF-2): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-154-basic | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1146-100 | Price: $253.00 | |
| Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 154 Basic (FGF-basic 154 / FGF-2): Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-154-basic | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1146-1000 | Price: $1,561.00 | |
| Dermal Fibroblast RNA (HDF RNA), Adult: Total RNA prepared from Human Dermal Fibroblasts, adult | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: 106-R10a | Price: $398.00 | |
| Dermal Fibroblast RNA (HDF RNA), Adult: Total RNA prepared from Human Dermal Fibroblasts, adult | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: 106-R25a | Price: $796.00 | |
| Dermal Fibroblast RNA (HDF RNA), Fetal: Total RNA prepared from Human Dermal Fibroblasts, fetal | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: 106-R10f | Price: $514.00 | |
| Dermal Fibroblast RNA (HDF RNA), Fetal: Total RNA prepared from Human Dermal Fibroblasts, fetal | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: 106-R25f | Price: $1,028.00 | |
| Dermal Fibroblast RNA (HDF RNA), Neonatal: Total RNA prepared from Human Dermal Fibroblasts, neonatal | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: 106-R10n | Price: $398.00 | |
| Dermal Fibroblast RNA (HDF RNA), Neonatal: Total RNA prepared from Human Dermal Fibroblasts, neonatal | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: 106-R25n | Price: $796.00 | |
| Human Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF): Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor | Size: 20 ug | CAT.#: RP1008-20 | Price: $194.00 | |
| Human Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF): Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1008-100 | Price: $484.00 | |
| Human Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF): Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1008-1000 | Price: $3,444.00 | |
| Human Gamma-Interferon Inducible Protein 10 (IP-10 / CXCL10): Human gamma-Interferon Inducible Protein 10 | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: RP1127-25 | Price: $194.00 | |
| Human Gamma-Interferon Inducible Protein 10 (IP-10 / CXCL10): Human gamma-Interferon Inducible Protein 10 | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1127-100 | Price: $484.00 | |
| Human Gamma-Interferon Inducible Protein 10 (IP-10 / CXCL10): Human gamma-Interferon Inducible Protein 10 | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1127-1000 | Price: $3,175.00 | |
| Human Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF): Human Migration Inhibitory Factor | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: RP1153-25 | Price: $194.00 | |
| Human Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF): Human Migration Inhibitory Factor | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1153-100 | Price: $484.00 | |
| Human Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF): Human Migration Inhibitory Factor | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1153-1000 | Price: $3,175.00 | |
| Human MIF ELISA Kit: Human Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor ELISA Kit | Size: 96 wells | CAT.#: CL0813 | Price: $511.00 | |
| Subculture Reagent Kit: 100 ml each of HBSS, Trypsin/EDTA & Trypsin Neutralizing Solution | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: 090K | Price: $63.00 | |
| Human GM-CSF, Animal-Free: Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor, Animal-Free | Size: 20 ug | CAT.#: RP1008AF-20 | Price: $213.00 | |
| Human GM-CSF, Animal-Free: Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor, Animal-Free | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1008AF-100 | Price: $533.00 | |
| Human GM-CSF, Animal-Free: Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor, Animal-Free | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1008AF-1000 | Price: $3,788.00 | |
| Human FGF-147 basic, Animal-Free: Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-basic-147, Animal-Free | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: RP1028AF-10 | Price: $89.00 | |
| Human FGF-147 basic, Animal-Free: Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-basic-147, Animal-Free | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1028AF-100 | Price: $347.00 | |
| Human FGF-147 basic, Animal-Free: Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-basic-147, Animal-Free | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1028AF-1000 | Price: $1,717.00 | |
| Human FGF-basic 154, Animal-Free: Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-basic-154, Animal-Free | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: RP1146AF-10 | Price: $89.00 | |
| Human FGF-basic 154, Animal-Free: Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-basic-154, Animal-Free | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1146AF-100 | Price: $276.00 | |
| Human FGF-basic 154, Animal-Free: Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-basic-154, Animal-Free | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1146AF-1000 | Price: $1,717.00 | |
| HDF Growth Medium wo Antibiotics: Growth medium without antibiotics | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 116A-500 | Price: $136.00 |
Resources/Documents
Citations
Publications
2017
Martinez-Cerdeno, Veronica, Bonnie Barrilleaux, Ashley McDonough, Jeanelle Ariza, Benjamin Yuen, Priyanka Somanath, Catherine Le, Craig Steward, Kayla Horton, and Paul Knoepfler. 2017. Behavior of xeno-transplanted undifferentiated human induced pluripotent stem cells is impacted by microenvironment without evidence of tumors. Stem Cells and Development. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2017.0059.
Y Esparza, A Ullah, Y Boluk, J Wu. 2017. Preparation and characterization of thermally crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol)/feather keratin nanofiber scaffolds. Materials & Design, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.07.052.
Cruz, L., N. Streck, K. Ferguson, T. Desai, D. Desai, S. Amin and N. Buchkovich. 2017. Potent Inhibition of HCMV by Modulating the Cellular SNARE Syntaxin 5. J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01637-16.
2016
Connor, B., D. Mirella and C. Maucksch. 2016. Cell Programming. Patent Application US 20160122712 A1.
Bellayr, I., R. Marklein, J. Lo Surdo, S. Bauer and R. Puri. 2016. Identification of Predictive Gene Markers for Multipotent Stromal Cell Proliferation. Stem Cells & Dev, 25:861-873.
Duncan, D., T. Kamerzell and M. Palmer. 2016. Use of Indole Compounds for Fat Reduction and Skin and Soft Tissue Tightening. Patent Application US 20160030389 A1.
Fujimori, C., J. Kumai, K. Nakamura, Y. Gu, F. Katagiri, K. Hozumi, Y. Kikkawa and M. Nomizu. 2016. Biological Activity of Peptide-conjugated Polyion Complex Matrices Consisting of Alginate and Chitosan. Peptide Science, 10.1002/bip.22983.
Kentaro, H., N. Kyotaro, H. Haruna, M. Mari, N. Rika, T. Keiko, K. Fumihiko, K. Yamato and N. Motoyoshi. 2016. Mixed Fibronectin-Derived Peptides Conjugated to a Chitosan Matrix Effectively Promotes Biological Activities through Integrins, α4β1, α5β1, αvβ3, and Syndecan. BioResearch Open Access, 5:356-366.
Lalli, M., J. Jang, J. Park, Y. Wang, E. Guzman, H. Zhou, M. Audouard, D. Bridges, K. Tovar, S. Papuc, A. Tutulan-Cunita, Y. Huang, M. Budisteanu, A. Arghir, and K. Kosik. 2016. Haploinsufficiency of BAZ1B contributes to Williams syndrome through transcriptional dysregulation of neurodevelopmental pathways. Human Molecular Genetics, 2016:1-13.
Mavuso, S., Y. Choonara, T. Marimuthu, P. Kumar, L. du Toit, P. Kondiah and V. Pillay. 2106. A Dual pH/Redox Responsive Copper-Ligand Nanoliposome Bioactive Complex for the Treatment of Chronic Inflammation. Int J Pharmaceutics, 509:348-359.
Nakajima, H., S. Terazawa, T. Niwano, Y. Yamamoto, G. Imokawa. 2016. The Inhibitory Effects of Anti-Oxidants on Ultraviolet-Induced Up-Regulation of the Wrinkling-Inducing Enzyme Neutral Endopeptidase in Human Fibroblasts. PLoS ONE, 11(9): e0161580.
Roshan, A., L. Dong, C. Alvan, J. Bart and H. Wenhu. Validation of Cross-Species Reactivity of the VEGF-A/PDGFRβ Bifunctional Antibody PF-06653157. J Ocular Pharmacol & Ther, 32:650-658.
Saito, K., T. Asai, K. Fujiwara, J. Sahara, H. Koguchi, N. Fukuda, M. Suzuki-Karasaki, M. Soma and Y. Suzuki-Karasaki. 2016. Tumor-selective mitochondrial network collapse induced by atmospheric gas plasma-activated medium. Oncotarget, impactjournals.com/oncotarget 1-18.
Sévin, D., J. Stählin, G. Pollak, A. Kuehne and U. Sauer. 2016. Global Metabolic Responses to Salt Stress in Fifteen Species. PLoS ONE 11(2):e0148888.
Sun, X, S. Chakrabarti, J. Fang, Y. Yin and J. Wu. 2016. Low Molecular-Weight Fractions of Alcalase Hydrolyzed Egg Ovomucin Extract Exert Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Human Dermal Fibroblasts through the Inhibition of TNF Mediated NF-κB Pathway. Nutrition Res, 36:648-657.
Teye, K. S. Numata, N. Ishii, R. Krol, A. Tsuchisaka, T. Hamada, H. Koga, T. Karashima, C. Ohata, D. Tsuruta, H. Saya, M. Haftek and T. Hashimoto. 2016. Isolation of All CD44 Transcripts in Human Epidermis and Regulation of Their Expression by Various Agents. PLOS ONE, 11(8): e0160952.
Yamakawa, T., Y. Sato, Y. Matsumura, Y. Kobayashi, Y. Kawamura, N. Goshima, S. Yamanaka, and K. Okita. 2016. Screening of Human cDNA Library Reveals Two differentiation-Related Genes, HHEX and HLX, as Promoters of Early Phase Reprogramming toward Pluripotency. Stem Cells, 34:2661-2669.
Yamanaka, S., K. Takahashi, K. Tanabe and M. Ohnuki. 2016. Method of Efficiently Establishing Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Patent Application US 2016 0122720 A1.
Zhu, X., A. Okubo, N. Igari, K. Ninomiya and Y. Egashira. 2016. Modified rice bran hemicellulose inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis in vitro via VEGFR2 and its downstream signaling pathways. Biosci of Microbiota, Food & Health, advpub_16-016.
2015
Alexandra, R., and S. Ramille. 2015. POLY(ETHYLENE GLYCOL) CROSS-LINKING OF SOFT MATERIALS TO TAILOR VISCOELASTIC PROPERTIES FOR BIOPRINTING. Patent Application 20150084232 A1.
Fiesel, F., M. Ando, R. Hudec, A. Hill, M. Castanedes-Casey, T. Caulfield, E. Moussaud-Lamodiere, J. Stankowski, P. Bauer, O. Lorenzo-Betancor, I. Ferrer, J. Arbelo, J. Siuda, L. Chen, V. Dawson, T. Dawson, Z. Wszolek, O. Ross, D. Dickson and W. Sp-ringer. 2015. (Patho-) physiological relevance of PINK1-dependent ubiquitin phosphorylation. EMBO Reports, 16:1114-1130.
Hiroe, O., K. Takashi, D. Tomonori and Y. Shunsuke. 2015. Generation of Xeroderma Pigmentosum-A Patient-Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Line for Use As Future Disease Model. Cellular Reprogramming, 17:268-274. HDF
Hozumi, K., C. Fujimori, F. Katagiri, Y. Kikkawa, M. Nomizu. 2015. Suppression of cell adhesion through specific integrin crosstalk on mixed peptide-polysaccharide matrices. Biomaterials, 37:73-81.
Kubat, N., J. Moffett, and L. Fray. 2015. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic field treatment on programmed resolution of inflammation pathway markers in human cells in culture. J Inflamm Res, 8:59-69.
Kumai, J., K. Hozumi, Y. Yamada, F. Katagiri, Y. Kikkawa and M. Nomizu. 2015. Effect of Spacer Length and Type on the Biological Activity of Peptide–Polysaccharide Matrices. Peptide Science 106:512-520.
Qu, T., J. Cheng, J. Sun, H. Yang, K. Cheng, and J. Shen. 2015. Methods of Attenuating Opioid Tolerance. Patent Application US 20150246074 A1.
Rutz, A., K. Hyland, A. Jakus, W. Burghardt, and R. Shah. 2015. A Multimaterial Bioink Method for 3D Printing Tunable, Cell-Compatible Hydrogels. Adv Mater, 27: 1607–1614.
Saito, K., N. Fukuda, K. Shinohara, Y. Masuhiro, S. Hanazawa, H. Matsuda, K. Fujiwara, T. Ueno and M. Soma. 2015. Modulation of the EMT/MET process by pyrrole–imidazole polyamide targeting human transforming growth factor-β1. Intl J Biochem & Cell Biol, 66:112-120.
Suzuki-Karasaki, Y., K. Fujiwara, K. Saito, M. Suzuki-Karasaki, T. Ochiai and M. Soma. 2015. Distinct effects of TRAIL on the mitochondrial network in human cancer cells and normal cells: role of plasma membrane depolarization. Oncotarget, 6:21572-21588.
Wren, M., J. Zhao, C. Liu, M. Murray, Y. Atagi, M. Davis, Y. Fu, H. Okano, K. Ogaki, A. Strongosky, P. Tacik, R. Rademakers, O. Ross, D. Dickson, Z. Wszolek, T. Kanekiyo, and G. Bu. 2015. Frontotemporal dementia-associated N279K tau mutant disrupts subcellular vesicle trafficking and induces cellular stress in iPSC-derived neural stem cells. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 10:46.
Yamanaka, S. and O. Keisuke. 2015. HIGHLY EFFICIENT METHOD FOR ESTABLISHING INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM CELL. US Patent Application 20150175973 A1.
Yamanaka, S. and K. Okita. 2015. Method of Nuclear Reprogramming. US Patent Application 20150072417 A1.
Yan, Y., M. Furumura, T. Gouya, A. Iwanaga, K. Teye, S. Numata, T. Karashima, X. Li, and T. Hashimoto. 2015. Shikonin Promotes Skin Cell Proliferation and Inhibits Nuclear Factor-κB Translocation via Proteasome Inhibition In Vitro. Chinese Medical Journal, 128:2228-2233.
2014
Baboolal, T., S. Boxall, Y. El-Sherbiny, T. Moseley, R. Cuthbert, P. Giannoudis, D. McGonagle and E. Jones. 2014. Multipotential stromal cell abundance in cellular bone allograft: comparison with fresh age-matched iliac crest bone and bone marrow aspirate. Regenerative Medicine, 9:593-607.
Becker, T., S. Boyd, B. Mijatov, K. Gowrishankar, S. Snoyman, G. Pupo, R. Scolyer, G. Mann, R. Kefford, X. Zhang and H. Rizos. 2014. Mutant B-RAF-Mcl-1 survival signaling depends on the STAT3 transcription factor. Oncogene, 33:1158-1166.
Haselmayer, P. M. Camps, M. Muzerelle, S. Bawab, C. Waltzinger, L. Bruns, N. Abla, M. Polokoff, C. Jond-Necand, M. Gaudet, A. Benoit, D. Meier, C. Martin, D. Gretener, M. Lombardi, R. Grenningloh, C. Ladel, J. Petersen, P. Gaillard, and H. Ji. 2014. Characterization of novel PI3Kδ inhibitors as potential therapeutics for SLE and lupus nephritis in pre-clinical studies. Front Immunol, 5:233.
Maekawa, M., K. Yamada, M. Yoyoshima, T. Ohnishi, Y. Iwayama, C. Shimamoto, T. Toyota, Y. Nozake, S. Balan, H. Matsuzaki, Y. Iwata, K. Suzuki, M. Miyashita, M. Kikuchi, M. Kato, Y. Okada, W. Akamatsu, N. Mori, Y. Owada, M. Itokawa, H. Okano, and T. Yoshikawa. 2014. Utility of Scalp Hair Follicles as a Novel Source of Biomarker Genes for Psychiatric Illnesses. Biological Psychiatry, Online 11 Sep.
Ohsumi, K., M. Watanabe, and A. Fujie. 2014. AS2077715 is a selective inhibitor of fungal mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex. The Journal of Antibiotics, 713–716.
Pandian, G.N., J. Taniguchi, S. Junetha, S. Sato, L. Han, A. Saha, C. Anandhakumar, T. Bando, H. Nagase, T. Vaijayanthi, R.D. Taylor, and H. Sugiyama. 2014. Distinct DNA-based epigenetic switches trigger transcriptional activation of silent genes in human dermal fibroblasts. Scientific reports. 4:3843.
Rolfes, E., J. Ross, J. McGonigle, G. Opperman and S. Chudzik. 2014. Poly-α(1→4)glucopyranose-based matrices with hydrazide crosslinking. Patent US8790701 B2.
2013
Koyanagi-Aoi, M., M. Ohnuki, K. Takahashi, K. Okita, H. Noma, Y. Sawamura, I. Teramoto, M. Narita, Y. Sato, T. Ichisaka, N. Amano, A. Watanabe, A. Morizane, Y. Yamada, T. Sato, J. Takahashi, and S. Yamanaka. 2013. Differentiation-defective phenotypes revealed by large-scale analyses of human pluripotent stem cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110:20569-20574.
Noguchi, M., K. Hosoda, M. Nakane, E. Mori, K. Nakao, D. Taura, Y. Yamamoto, T. Kusakabe, M. Sone, H. Sakurai, J. Fujikura, K. Ebihara, and K. Nakao. 2013. In vitro characterization and engraftment of adipocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells and embryonic stem cells. Stem cells and development. 22:2895-2905.
Okita, K., T. Yamakawa, Y. Matsumura, Y. Sato, N. Amano, A. Watanabe, N. Goshima, and S. Yamanaka. 2013. An Efficient Nonviral Method to Generate Integration‐Free Human‐Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Cord Blood and Peripheral Blood Cells. Stem cells. 31:458-466.
Otagiri, D., Y. Yamada, K. Hozumi, F. Katagiri, Y. Kikkawa, and M. Nomizu. 2013. Cell attachment and spreading activity of mixed laminin peptide–chitosan membranes. Peptide Science. 100:751-759.
Razak, S.R.A., K. Ueno, N. Takayama, N. Nariai, M. Nagasaki, R. Saito, H. Koso, C.-Y. Lai, M. Murakami, and K. Tsuji. 2013. Profiling of MicroRNA in Human and Mouse ES and iPS Cells Reveals Overlapping but Distinct MicroRNA Expression Patterns. PloS one. 8:e73532.
Sato, M., S.-i. Maeda, E. Inada, I. Saitoh, and N. Kubota. 2013. Mosaic Expression of Pluripotency-Related Proteins Oct-3/4 and Alkaline Phosphatase in Human Pancreatic Carcinoma Cell PANC-1. Advanced Studies in Biology. 5:157-172.
Tanaka, A., K. Woltjen, K. Miyake, A. Hotta, M. Ikeya, T. Yamamoto, T. Nishino, E. Shoji, A. Sehara-Fujisawa, Y. Manabe, N. Fujii, K. Hanaoka, T. Era, S. Yamashita, K.-i. Isobe, E. Kimura, and H. Sakurai. 2013. Efficient and Reproducible Myogenic Differentiation from Human iPS Cells: Prospects for Modeling Miyoshi Myopathy In Vitro. PloS one. 8:e61540.
Yamada, Y., K. Hozumi, F. Katagiri, Y. Kikkawa, and M. Nomizu. 2013. Laminin-111-derived peptide-hyaluronate hydrogels as a synthetic basement membrane. Biomaterials. 34:6539-6547.
Yanagida, A., K. Ito, H. Chikada, H. Nakauchi, and A. Kamiya. 2013. An In Vitro Expansion System for Generation of Human iPS Cell-Derived Hepatic Progenitor-Like Cells Exhibiting a Bipotent Differentiation Potential. PloS one. 8:e67541.
Zheng Q, C.S., Chen Y, Lyga J, Wyborski R, Santhanam U. 2013. Investigation of age-related decline of microfibril-associated glycoprotein-1 in human skin through immunohistochemistry study. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology. 6:317-323.
2012
Dell’Agli, M., C. Sanna, P. Rubiolo, N. Basilico, E. Colombo, M.M. Scaltrito, M.O. Ndiath, L. Maccarone, D. Taramelli, and C. Bicchi. 2012. Anti-plasmodial and insecticidal activities of the essential oils of aromatic plants growing in the Mediterranean area. Malaria journal. 11:1-10.
Hara, R., and H. Kawaguchi. 2012. Highly Sensitive Detection of Telomerase by Using G-Quartet DNA Binder Conjugated Polymeric Microspheres. Kobunshi Ronbunshu, 69:122-128.
Hozumi, K., A. Sasaki, Y. Yamada, D. Otagiri, K. Kobayashi, C. Fujimori, F. Katagiri, Y. Kikkawa, and M. Nomizu. 2012. Reconstitution of laminin-111 biological activity using multiple peptide coupled to chitosan scaffolds. Biomaterials. 33:4241-4250.
Hozumi, K., M. Ishikawa, T. Hayashi, Y. Yamada, F. Katagiri, Y. Kikkawa, and M. Nomizu. 2012. Identification of cell adhesive sequences in the N-terminal region of the laminin α2 chain. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287:25111-25122.
Kato, Y., Y. Katagata, M. Goto, K. Yamamoto, M. Maeda, Y. Hanada, M. Takai, and Y. Suekawa. 2012. Extract of aquatic animal cartilage. Patent Application US 20130310540 A1.
Ko, P. 2012. Cosmetic and dermatological formulations of MNTF peptides. Patent US 8334253 B2.
Mahasiripanth, T., S. Hokputsa, S. Niruthisard, P. Bhattarakosol, and S. Patumraj. 2012. Effects of Acanthus ebracteatus Vahl on tumor angiogenesis and on tumor growth in nude mice implanted with cervical cancer. Cancer management and research. 4:269.
Matsui, T., M. Takano, K. Yoshida, S. Ono, C. Fujisaki, Y. Matsuzaki, Y. Toyama, M. Nakamura, H. Okano, and W. Akamatsu. 2012. Neural Stem Cells Directly Differentiated from Partially Reprogrammed Fibroblasts Rapidly Acquire Gliogenic Competency. Stem cells. 30:1109-1119.
Maucksch, C., E. Firmin, C. Butler-Munro, J. Montgomery, M. Dottori, andn B. Connor. 2012. Non-Viral Generation of Neural Precursor-like Cells from Adult Human Fibroblasts. J Stem Cells Regen Med, 8:162-170.
Moffett, J., L.M. Fray, and N.J. Kubat. 2012. Activation of endogenous opioid gene expression in human keratinocytes and fibroblasts by pulsed radiofrequency energy fields. Journal of pain research. 5:347.
Oda, Y., H. Ohnishi, S. Yuba, and H. Ohgushi. 2012. Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Derived from Human Third Molars (Method). Stem Cells and Cancer, 2:83-93.
Ohta, K. 2012. Method for producing pluripotent cell using bacterium having fermentation ability. Patent Aplication US 20140255942 A1.
Ohta, K., R. Kawano, and N. Ito. 2012. Lactic acid bacteria convert human fibroblasts to multipotent cells. PloS one. 7:e51866-e51866.
Ono, Y., Y. Wang, H. Suzuki, S. Okamoto, Y. Ikeda, M. Murata, M. Poncz, and Y. Matsubara. 2012. Induction of functional platelets from mouse and human fibroblasts by p45NF-E2/Maf. Blood. 120:3812-3821.
Rapko, S., and S. Duguay. 2012. Methods of evaluating cells and cell cultures. Patent Application US 20120329051 A1.
Rim, J.S., K.L. Strickler, C.W. Barnes, L.L. Harkins, J. Staszkiewicz, J.M. Gimble, G.H. Leno, and K.J. Eilertsen. 2012. Temporal epigenetic modifications differentially regulate ES cell-like colony formation and maturation. Stem Cell Discovery. 2:45-57.
Sakurai, H., Y. Sakaguchi, E. Shoji, T. Nishino, I. Maki, H. Sakai, K. Hanaoka, A. Kakizuka, and A. Sehara-Fujisawa. 2012. In Vitro Modeling of Paraxial Mesodermal Progenitors Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. PloS one. 7:e47078.
Yamanaka, S., K. Takahashi, and K. Okita. 2012. Somatic cell reprogramming by retroviral vectors encoding Oct3/4. Klf4, c-Myc and Sox2. Patent US 8129187 B2.
Yamanaka, S., K. Takahashi, and K. Okita. 2012. Induced pluripotent stem cells produced with Oct3/4, Klf4 and Sox2. Patent US 8278104 B2.
Yamanaka, S., K. Takahashi, and K. Okita. 2012. Induced pluripotent stem cells produced with oct3/4, klf and sox. Patent Application US 20130059386 A1.
2011
Connor, B., M. Dottori, and C. Maucksch. 2011. Cell programming. Patent Application US 20120301965 A1.
Deneau, J., T. Ahmed, R. Blotsky, and K. Bojanowski. 2011. Anti-diabetic activity of a mineraloid isolate, in vitro and in genetically diabetic mice. International journal for vitamin and nutrition research. Internationale Zeitschrift fur Vitamin- und Ernahrungsforschung. Journal international de vitaminologie et de nutrition. 81:34-42.
Gao, Z., M.S. Xu, T.L. Barnett, and C.W. Xu. 2011. Resveratrol induces cellular senescence with attenuated mono-ubiquitination of histone H2B in glioma cells. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 407:271-276.
Hirai, H., T. Tani, N. Katoku-Kikyo, S. Kellner, P. Karian, M. Firpo, and N. Kikyo. 2011. Radical Acceleration of Nuclear Reprogramming by Chromatin Remodeling with the Transactivation Domain of MyoD. Stem cells. 29:1349-1361.
Iwabuchi, K., T. Yamakawa, Y. Sato, T. Ichisaka, K. Takahashi, K. Okita, and S. Yamanaka. 2011. ECAT11/L1td1 Is Enriched in ESCs and Rapidly Activated During iPSCGeneration, but It Is Dispensable for the Maintenance and Induction of Pluripotency. PLOS One, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020461.
Moffett, J., N.J. Kubat, N.E. Griffin, M.C. Ritz, and F.R. George. 2011. Pulsed radio frequency energy field treatment of cells in culture: Increased expression of genes involved in angiogenesis and tissue remodeling during wound healing. The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications. 3:30-39.
Ohta, S., Y. Imaizumi, Y. Okada, W. Akamatsu, R. Kuwahara, M. Ohyama, M. Amagai, Y. Matsuzaki, S. Yamanaka, and H. Okano. 2011. Generation of human melanocytes from induced pluripotent stem cells. PloS one. 6:e16182.
Rapko, S., and S. Duguay. 2011. Methods of evaluating cells and cell cultures. Patent Application US 20120149013 A1.
Suzuki, M., M. Kitagawa, S. Yamamoto, A. Sogabe, D. Kitamoto, T. Morita, T. Fukuoka, and T. Imura. 2011. Activator including biosurfactant as active ingredient, mannosyl erythritol lipid, and production method thereof. Patent Application US 20120070396 A1.
Yamanaka, S., and K. Takahashi. 2011. Oct3/4, Klf4, c-Myc and Sox2 produce induced pluripotent stem cells. Patent US 8058065 B2.
Yamanaka, S., K. Takahashi, and K. Tanabe. 2011. Efficient method for establishing induced pluripotent stem cells. Patent US 20130267030 A1.
2010
Hayashi, Y., T. Chan, M. Warashina, M. Fukuda, T. Ariizumi, K. Okabayashi, N. Takayama, M. Otsu, K. Eto, M.K. Furue, T. Michiue, K. Ohnuma, H. Nakauchi, and M. Asashima. 2010. Reduction of N-Glycolylneuraminic Acid in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Generated or Cultured under Feeder- and Serum-Free Defined Conditions. PloS one. 5:e14099.
Li, G., C. Luna, J. Qiu, D.L. Epstein, and P. Gonzalez. 2010. Targeting of integrin β1 and kinesin 2α by microRNA 183. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 285:5461-5471.
Moffett, J., N. Griffin, M. Ritza, and F. George. 2010. Pulsed radio frequency energy field treatment of cells in culture results in increased expression of genes involved in the inflammation phase of lower extremity diabetic wound healing. J Diabetic Foot Complications, 2:57-64.
Nomoto, Y., W. Okano, M. Imaizumi, A. Tani, S. Sato, M. Nomoto, and K. Omori. 2010. Regeneration and Repair Mechanism of the Larynx and Trachea with Hybrid Artificial Scaffold. Koutou, 22:71-76.
Oda, Y., Y. Yoshimura, H. Ohnishi, M. Tadokoro, Y. Katsube, M. Sasao, Y. Kubo, K. Hattori, S. Saito, K. Horimoto, S. Yuba, and H. Ohgushi. 2010. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from human third molar mesenchymal stromal cells. The Journal of biological chemistry. 285:29270-29278.
Rapko, S., M. Zhang, B. Richards, E. Hutto, S. Dethlefsen, and S. Duguay. 2010. Identification of the Chondrocyte Lineage Using Microfibril-Associated Glycoprotein-2, A Novel Marker That Distinguishes Chondrocytes from Synovial Cells. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 16:1367-1375.
Salamone, J., A. Salamone, and M. Lowe. 2010. Conformable bandage and coating material. Patent US 7795326 B2.
Scurr, L.L., G.M. Pupo, T.M. Becker, K. Lai, D. Schrama, S. Haferkamp, M. Irvine, R.A. Scolyer, G.J. Mann, and J.C. Becker. 2010. IGFBP7 is not required for B-RAF-induced melanocyte senescence. Cell. 141:717-727.
Suganuma, K., H. Nakajima, M. Ohtsuki, and G. Imokawa. 2010. Astaxanthin attenuates the UVA-induced up-regulation of matrix-metalloproteinase-1 and skin fibroblast elastase in human dermal fibroblasts. Journal of dermatological science. 58:136-142.
Takayama, N., S. Nishimura, S. Nakamura, T. Shimizu, R. Ohnishi, H. Endo, T. Yamaguchi, M. Otsu, K. Nishimura, and M. Nakanishi. 2010. Transient activation of c-MYC expression is critical for efficient platelet generation from human induced pluripotent stem cells. The Journal of experimental medicine. 207:2817-2830.
Wilmink, G., B. Rivest, B. Ibey, C. Roth, J. Bernhard, and W. Roach. 2010. Quantitative Investigation of the Bioeffects Associated with Terahertz Radiation. Optical Interactions with Tissues and Cells XXI, edited by E. Duco Jansen, Robert J. Thomas, Proc. of SPIE Vol 7562, 75620L. doi: 10.1117/12.844916.
Xu, C. 2010. Reprogramming of somatic cells with purified proteins. Patent Application US 20120115225 A1.
Yamanaka, S. 2010. Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells. Patent Application US 20100210014 A1.
Yamanaka, S. 2010. Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells. Patent Application US 20100216236 A1.
Yamauchi, Y., E. Tsuruga, K. Nakashima, Y. Sawa, and H. Ishikawa. 2010. Fibulin-4 and-5, but not fibulin-2, are associated with tropoelastin deposition in elastin-producing cell culture. Acta histochemica et cytochemica. 43:131.
Yamazaki, C.M., Y. Kadoya, K. Hozumi, H. Okano-Kosugi, S. Asada, K. Kitagawa, M. Nomizu, and T. Koide. 2010. A collagen-mimetic triple helical supramolecule that evokes integrin-dependent cell responses. Biomaterials. 31:1925-1934.
Vrba, L., T.J. Jensen, J.C. Garbe, R.L. Heimark, A.E. Cress, S. Dickinson, M.R. Stampfer, and B.W. Futscher. 2010. Role for DNA Methylation in the Regulation of miR-200c and miR-141 Expression in Normal and Cancer Cells. PloS one. 5:e8697.
2009
Choi, S. 2009. Die Rolle der Aurora-A Polymorphismen in der Pathogenese des Multiplen Myeloms. German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, dissertation.
Del Carmen Velazquez Pereda, M., G. De Campos Dieamant, S. Eberlin, C. Nogueira, D. Colombi, L.C. Di Stasi, and M.L. De Souza Queiroz. 2009. Effect of green Coffea arabica L. seed oil on extracellular matrix components and water-channel expression in in vitro and ex vivo human skin models. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. 8:56-62.
Fusaki, N., H. Ban, A. Nishiyama, K. Saeki, and M. Hasegawa. 2009. Efficient induction of transgene-free human pluripotent stem cells using a vector based on Sendai virus, an RNA virus that does not integrate into the host genome. Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Series B. 85:348-362.
Gupta, A., C. Lobocki, S. Singh, M. Robertson, O.A. Akadiri, G. Malhotra, and I.T. Jackson. 2009. Actions and Comparative Efficacy of Phosphatidylcholine Formulation and Isolated Sodium Deoxycholate for Different Cell Types. Aesth Plast Surg. 33:346-352.
Haferkamp, S., L.L. Scurr, T.M. Becker, M. Frausto, R.F. Kefford, and H. Rizos. 2009. Oncogene-induced senescence does not require the p16INK4a or p14ARF melanoma tumor suppressors. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 129:1983-1991.
Kitazawa, H., Y. Kasukabe, and M. Kitagawa. 2009. Stress-reducing agent including plant-derived polyamine-containing extract serving as active component. Patent Application US 20110236512 A1.
Li, G., C. Luna, J. Qiu, D.L. Epstein, and P. Gonzalez. 2009. Alterations in microRNA expression in stress-induced cellular senescence. Mechanisms of ageing and development. 130:731-741.
Ohnuki, M., K. Takahashi, and S. Yamanaka. 2009. Generation and characterization of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Current Protocols in Stem Cell Biology, 1Jun, DOI: 10.1002/9780470151808.sc04a02s9.
Panja, A. 2009. Drug Discovery Methods Involving A Preclinical, In Vitro Isolated Gastrointestinal Epithelial Stem Cell-Like Progenitor Cell System. Patent Application US 20090269769 A1.
Suizu, F., Y. Hiramuki, F. Okumura, M. Matsuda, A.J. Okumura, N. Hirata, M. Narita, T. Kohno, J. Yokota, M. Bohgaki, C. Obuse, S. Hatakeyama, T. Obata, and M. Noguchi. 2009. The E3 Ligase TTC3 Facilitates Ubiquitination and Degradation of Phosphorylated Akt. Developmental Cell. 17:800-810.
Takahashi, K., M. Narita, M. Yokura, T. Ichisaka, and S. Yamanaka. 2009. Human induced pluripotent stem cells on autologous feeders. PloS one. 4:e8067.
Tsubooka, N., T. Ichisaka, K. Okita, K. Takahashi, M. Nakagawa, and S. Yamanaka. 2009. Roles of Sall4 in the generation of pluripotent stem cells from blastocysts and fibroblasts. Genes to Cells. 14:683-694.
Yamanaka, S., and K. Okita. 2009. Method of nuclear reprogramming. Patent Application US 20100279404 A1.
2008
Abdull Razis, A., E. Ismail, Z. Hambali, M. Abdullah, A. Ali, and M. Mohd Lila. 2008. Expression of Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor in Escherichia coli and Characterization of its Biological Activity. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 144:249-261.
Blackwell, T., M. Matsumoto, T. Makino, M. Goto, A. Ishikado, M. Maeda, and S. Azechi. 2008. Phase ii detoxification and antioxidant activity. Patent Application US 20110091587 A1.
Nakagawa, M., M. Koyanagi, K. Tanabe, K. Takahashi, T. Ichisaka, T. Aoi, K. Okita, Y. Mochiduki, N. Takizawa, and S. Yamanaka. 2008. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells without Myc from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nat Biotech. 26:101-106.
Pappas, J., and P. Yang. 2008. Human ESC vs. iPSC—Pros and Cons. J Cardiovascular Translational Res, 1:96-99.
Razis, A., E. Ismail, Z. Hambali, M. Abdullah, A. Ali, and M. Lila. 2008. Expression of Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor in Escherichia coli and Characterization of its Biological Activity. Appl Biochem and Biotech, 144:249-261.
Shiota, M., H. Izumi, T. Onitsuka, N. Miyamoto, E. Kashiwagi, A. Kidani, A. Yokomizo, S. Naito, and K. Kohno. 2008. Twist Promotes Tumor Cell Growth through YB-1 Expression. Cancer research. 68:98-105.
2006
Behera, A.K., E. Hildebrand, J. Szafranski, H.H. Hung, A.J. Grodzinsky, R. Lafyatis, A.E. Koch, R. Kalish, G. Perides, and A.C. Steere. 2006. Role of aggrecanase 1 in Lyme arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 54:3319-3329.
Cha, H.S., S. Rosengren, D.L. Boyle, and G.S. Firestein. 2006. PUMA regulation and proapoptotic effects in fibroblast‐like synoviocytes. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 54:587-592.
Cochran, S., B. Marshall, T. Barrows, Y. Su, and R. Schlicher. 2006. Hair grafts derived from plucked hair. Patent Application US 20070122387 A1.
2005
Ando, T., J. Ichikawa, A. Okamoto, K. Tasaka, A. Nakao, and Y. Hamada. 2005. Gemcitabine inhibits viability, growth, and metastasis of osteosarcoma cell lines. Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 23:964-969.
George, F. and J. Moffett. 2005. Electromagnetic activation of gene expression and cell growth. Patent Application 20050059153 A1.
Sasaki, M., Y. Kato, H. Yamada, and S. Terada. 2005. Development of a novel serum-free freezing medium for mammalian cells using the silk protein sericin. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry. 42:183-188.
2004
George, F., and J. Moffett. 2004. Using electromagnet energy to propagate and stimulate cell growth; regenerative medicine; wound healing agents; tissue engineering and treatment of skin disorders. Patent US 20050059153 A1.
2002
Xu, M., T. Okada, H. Sakai, N. Miyamoto, Y. Yanagisawa, A.E. MacKenzie, S. Hadano, and J.-E. Ikeda. 2002. Functional human NAIP promoter transcription regulatory elements for the NAIP and ΨNAIP genes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Structure and Expression. 1574:35-50.