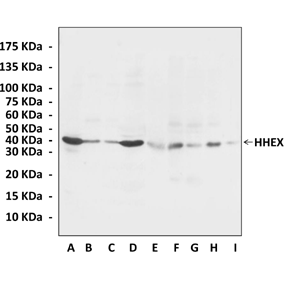
Anti-HHEX/PRH: Rabbit HHEX/PRH Anitbody
Price: $0.00
Description
The HHEX/PRH protein consists of three regions: a proline-rich N-terminal domain, a central homeodomain and an acidic C-terminal domain. The proline-rich N-terminal domain of PRH can make multiple protein–protein interactions and binds to several proteins including PML (promyelocytic leukaemic), eIF-4E, proteosome subunit HC8 and members of the Groucho/TLE family of co-repressor proteins. The N-terminal domain of HHEX/PRH is required for oligomerization and transcriptional repression and can influence the DNA-binding activity of the HHEX/PRH homeodomain. As well as binding to DNA, the HHEX/PRH homeodomain is important in HHEX/PRH oligomerization and forms protein–protein interactions with other transcription factors. The C-terminal domain of HHEX/PRH is rich in acidic residues but appears to play no role in repression; however, both the homeodomain and C-terminal domain are reported to play a role in transcription activation by HHEX/PRH. It was demonstrated that HHEX/PRH interacts with protein kinase CK2β and CK2 phosphorylates HHEX/PRH in vitro and in cells and that phosphorylation inhibits the DNA-binding activity of HHEX/PRH. Two amino acids within this the homeodomain that are phosphorylated by CK2: Ser163 and Ser177.3 Decreased HHEX/PRH expression and loss of nuclear localization of HHEX/PRH is implicated in a number of human myeloid leukaemias. In addition, a chromosomal translocation resulting in a HHEX/PRH fusion protein that can activate transcription and has trans-dominant-negative activity over wild-type HHEX/PRH has been shown to be a causative agent in acute myeloid leukaemia. Moreover, HHEX/PRH gene polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes.4
2. Soufi, A. & Jayaraman, P-S.: Biochem. J. 412:399-413, 2008
3. Soufi, A. et al: Nucl. Acids Res. 37:3288-300, 2009
4. van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, J. V. et al: Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 16:652-6, 2008
Details
| Cat.No.: | CA1326 |
| Antigen: | Short peptide from human HHEX/PRH N-terminal sequence. |
| Isotype: | Rabbit IgG |
| Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 – 1:200 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
| Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 40 kDa |
| Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of HHEX/PRH proteins without cross-reactivity with other related proteins. |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.