Anti-Lamin-B: Rabbit Lamin-B Antibody
Rabbit Lamin-B Antibody: Rabbit Lamin-B Antibody
Size: 100 ul
Price: $375.00
Description
In vertebrates, lamins are classified as A or B type, based on sequence homology, expression pattern, biochemical properties, and localization during mitosis. The A-type lamins, lamins A and C, are synthesized from alternatively spliced transcripts of LMNA and are expressed in most differentiated cells. Somatic cells also express two B-type lamins, lamin B1 and lamin B2, which are encoded by LMNB1 and LMNB2, respectively.2 Although the A- and B-type lamins interact with an overlapping set of other nuclear envelope proteins, they exhibit distinct expression patterns and different assembly properties, suggesting independent functions. For example, B-type lamins are expressed throughout development, whereas A-type lamins are expressed only after commitment of cells to a particular differentiation pathway. Also, A- and B-type lamins exhibit distinct solubility properties during mitosis because of temporal differences in the association with chromatin, with the association of B-type lamins preceding that of the A-type lamins. Mitotic spindle morphogenesis is a series of highly coordinated movements that lead to chromosome segregation and cytokinesis. It was demonstrated that lamin B assembled into a matrix-like network in mitosis through a process that depended on the presence of the guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-bound form of the small GTPase Ran. Depletion of lamin B resulted in defects in spindle assembly. Furthermore, lamin B was essential for the formation of the mitotic matrix that tethers a number of spindle assembly factors. Thus, it is suggested that lamin B is a structural component of the long-sought-after spindle matrix that promotes microtubule assembly and organization in mitosis.3 The lamin B receptor (LBR) is an integral membrane protein of the inner nuclear membrane that has so far been characterized only in vertebrates. The nucleoplasmic domain of LBR binds to B-type lamins, DNA, chromosomes and chromatin, and interacts with human chromodomain protein HP1 and nuclear membrane.4
2. Goldberg, M. et al: Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 9:285-93, 1999
3. Tsai, M.Y. et al: Science 311:1887-93,2006
4. Wagner, N. et al: J. Cell Sci. 117:2015-28, 2004
Details
| Cat.No.: | CA1048 |
| Antigen: | Short peptide from human Lamin-B sequence. |
| Isotype: | Rabbit IgG |
| Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Rat |
| Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 – 1:200 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
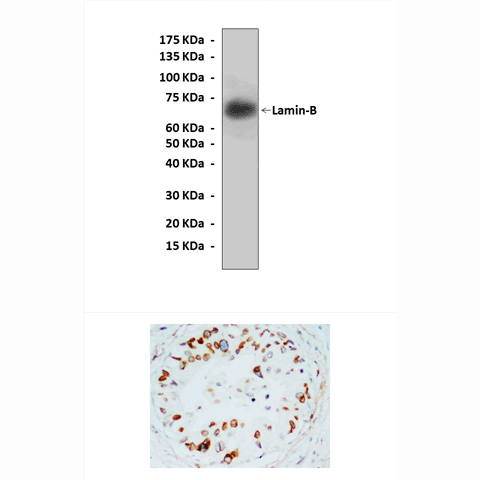
| Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 70 kDa |
| Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of lamin-B proteins without cross-reactivity with other related proteins. |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.