Anti-PDK1: Mouse PDK1 Antibody
Mouse PDK1 Antibody: Mouse PDK1 Antibody
Size: 100 ul
Price: $457.00
Description
PDK1 seems to exist in an active, phosphorylated configuration under basal conditions and appears to be refractive to additional activation and phosphorylation upon cell stimulation with agonists which activate PI-3 kinase. PDK1 itself is also an AGC kinase member and, like its substrates, requires to be phosphorylated at its T-loop (Ser-241) to be activated. In vivo, PDK1 is capable of autophosphorylation at Ser-241 by an intermolecular reaction and is thus constitutively phosphorylated at Ser-241. The structural analysis of the PDK1 kinase domain has revealed that, similar to what has been observed in other kinases, the phosphorylated Ser-241 residue forms key interactions coordinating and aligning important catalytic motifs such as the alphaC-helix of the N-terminal lobe.2 The alphaC-helix plays a key role in all kinases as it contributes crucial residues to coordinating ATP. More recently the structure of PKBbeta in the unphosphorylated, inactive state was reported to possess a completely disordered alphaC-helix. PDK1-mediated phosphorylation of PKBbeta and interaction of PKBbeta with its own hydrophobic motif (HM) led to ordering of this helix, resulting in PKB activation. This suggested a new regulatory alphaC-helix-dependent mechanism in PKB. PDK1 is activated through interaction with its substrates too.3 It is controversial whether PDK1 translocates to the plasma membrane in response to growth-factor stimulation. One study reported that PDK1 translocated to the membranes of endothelial cells in response to platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). PDK1 appears to be excluded from the nucleus in both stimulated and unstimulated cells. However, it was shown that PC-3 cells expressed phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated PDK-1 in the cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. In contrast, neuronal PDK-1 was located in the nucleoplasm and the phosphorylated form was located along the perinuclear region. Furthermore, it was reported that IGF-I transiently increased phosphorylation of neuronal PDK-1, resulting in its translocation to other cellular compartments.4
2. Casamayor, A. et al: Biochem. J. 342(Pt.2):287-92, 1999
3. Komander, D. et al: EMBO J. 23:3918-28, 2004
4. Alajajian, B,P. et al: Neuroreport 20:579-83, 2009
Details
| Cat.No.: | CP10363 |
| Antigen: | Raised against recombinant human PDK1 fragments expressed in E. coli. |
| Isotype: | Mouse IgG1 |
| Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
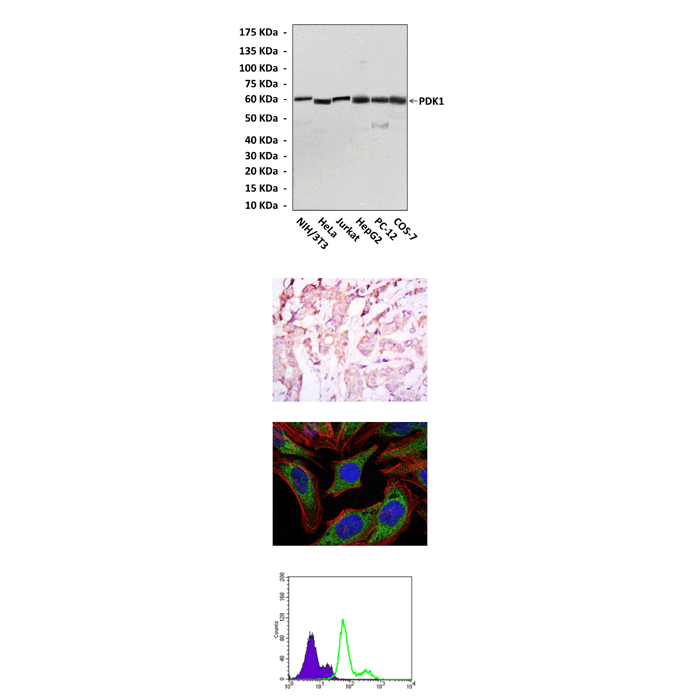
| Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 – 1:200 ICC 1:50 – 1:200 FACS 1:50 – 1:200 |
| Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 58-68 kDa |
| Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects PDK1 proteins in various cell lysate. |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.