IL-13 ELISA Kit, Mouse
Mouse IL-13 ELISA Kit: Mouse Interleukin-13 ELISA Kit
Size: 96 Wells
Price: $500.00
Description
IL-13 shares many functional properties with IL-4, stemming from the fact that they share a common receptor subunit, the alpha subunit of the IL-4 receptor (IL-4Ralpha). Characterization of IL-13-deficient mice, IL-4-deficient mice, and IL-4 receptor alpha-deficient (IL-4Ralpha(-/-)) mice have demonstrated nonredundant roles for IL-13. IL-13 mediates its effects by interacting with a complex receptor system comprised of IL-4Ralpha and two IL-13 binding proteins, IL-13Ralpha1 and IL-13Ralpha2. IL-13 receptors are expressed on human B cells, basophils, eosinophils, mast cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, monocytes, macrophages, respiratory epithelial cells, and smooth muscle cells. However, functional IL-13 receptors have not been demonstrated on human or mouse T cells. Thus unlike IL-4, IL-13 does not appear to be important in the initial differentiation of CD4 T cells into Th2-type cells but rather appears to be important in the effector phase of allergic inflammation. IL-13 sequentially binds to IL-13Ralpha1 and IL-4Ralpha forming a high affinity signaling complex. This receptor complex signals through STAT-6 to stimulate the production of chemokines, cytokines and mucus.2 Moreover, IL-13Ralpha2 has a high affinity for IL-13 but is insufficient to render cells responsive to IL-13 even in the presence of IL-4Ralpha. IL-13Ralpha2 has a short cytoplasmic tail that lacks box 1 and box 2 signaling motifs, suggesting that it has no direct signaling ability. Indeed, characterization of IL-13Ralpha2-deficient mice has revealed that IL-13Ralpha2 can downregulate IL-13 responses by sequestering IL-13, although there is evidence that IL-13Ralpha2 may contribute to IL-13-induced TGF-beta1-dependent fibrosis. In mice, IL-13Ralpha2 exists in soluble (s) and membrane (mem) forms, which can both bind to IL-13 and modulate its activity. Furthermore, IL-13Ralpha2 was found to be overexpressed in many tumor cells, thus it is also being targeted in cancer models by novel approaches.3 Given the importance of IL-13 as an effector molecule, regulation at the level of its receptors might be an important mechanism of modulating IL-13 responses and thus propagation of the allergic response. Accordingly, IL-13 is an attractive, novel therapeutic target for pharmacologic intervention in allergic disorders.4
2. Roy, B. et al: J. Leukoc. Biol. 72:580-9, 2002
3. Joshi, B.H. & Puri, R.K.: Immunotherapy 1:321-7, 2009
4. Martin, P.L. et al: Int J Toxicol. 27:351-8, 2008
Details
| Cat.No.: | CL0425 |
| Target Protein Species: | Mouse |
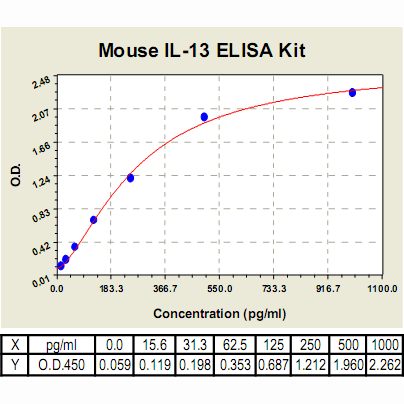
| Range: | 15.6 pg/ml – 1000pg/ml |
| Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokines |
| Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |