P-Cadherin ELISA Kit, Human
Human P-Cadherin ELISA Kit: Human P-Cadherin ELISA Kit
Size: 96 wells
Price: $554.00
Description
P-cadherin (CDH3) is a 118-kd transmembrane glycoprotein and first identified in mouse placenta. It is composed of 5 extracellular domains, designated EC1–EC5, a transmembrane domain and a small intracellular domain. The extracellular domains, mainly EC1, are crucial to the normal alignment of the protein in order to form the appropriate adhesive interactions with nearby cells. The EC domains contain calcium-binding regions that are imperative for their normal functioning. The intracellular domain of P-cadherin interacts with beta-catenin, which binds, indirectly through alpha-catenin, to the actin filament-binding proteins and other actin-binding proteins and functions in maintaining the cytoskeleton of the cells. More importantly, beta-catenin is involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, influencing many developmental processes. The function of P-cadherin is not restricted to the formation of adherens junctions but is also involved in other biological processes, such as cell recognition, cell signaling, morphogenesis and tumor development.3 In human its expression is not detectable in the placenta but is present in a few organs, such as mammary gland and prostate. E-Cadherin is expressed in most epithelial cells, whereas P-cadherin is restricted to basal cell layers, including basal cells of skin and prostate and myoepithelial cells of the mammary gland. In addition to maintaining cellular adhesion, P-cadherin plays important role in cell differentiation and proliferation.2 It was shown that P-cadherin expression pattern has been linked to a more dedifferentiated stem-cell-related population of tumor cells. Up-regulation of P-cadherin has been shown in several lesions, including breast cancer, in which there is usually down-regulation of E-cadherin. Breast carcinomas show aberrant P-cadherin expression in ∼30% of the cases and has been reported as a prognostic marker of poor outcome in patients. It was shown that P-cadherin overexpression, in breast cancer cells promotes cell invasion, motility and migration. Moreover, the overexpression of P-cadherin induces the secretion of matrix metalloproteases, specifically MMP-1 and MMP-2, which then lead to P-cadherin ectodomain cleavage. Furthermore, soluble P-cadherin fragment is able to induce in vitro invasion of breast cancer cells.4 Mutations in P-cadherin could result in development hypotrichosis with juvenile macular dystrophy (HJMD).
2. Shimomura, Y. et al: Dermatol. 220:208-12, 2010
3. Takeichi, M. et al: Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 7:619-27, 1995
4. Ribeiro, A.S. et al: Oncogene 29:392-402, 2010
Details
| Cat.No.: | CL0667 |
| Target Protein Species: | Human |
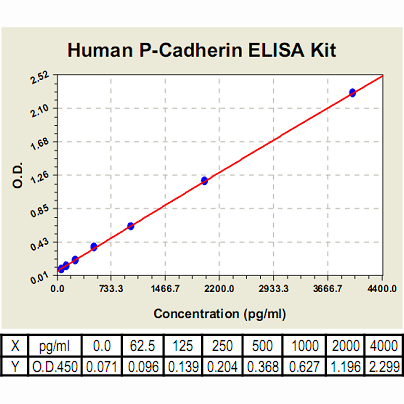
| Range: | 62.5pg/ml-4, 000pg/ml |
| Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokine. |
| Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |