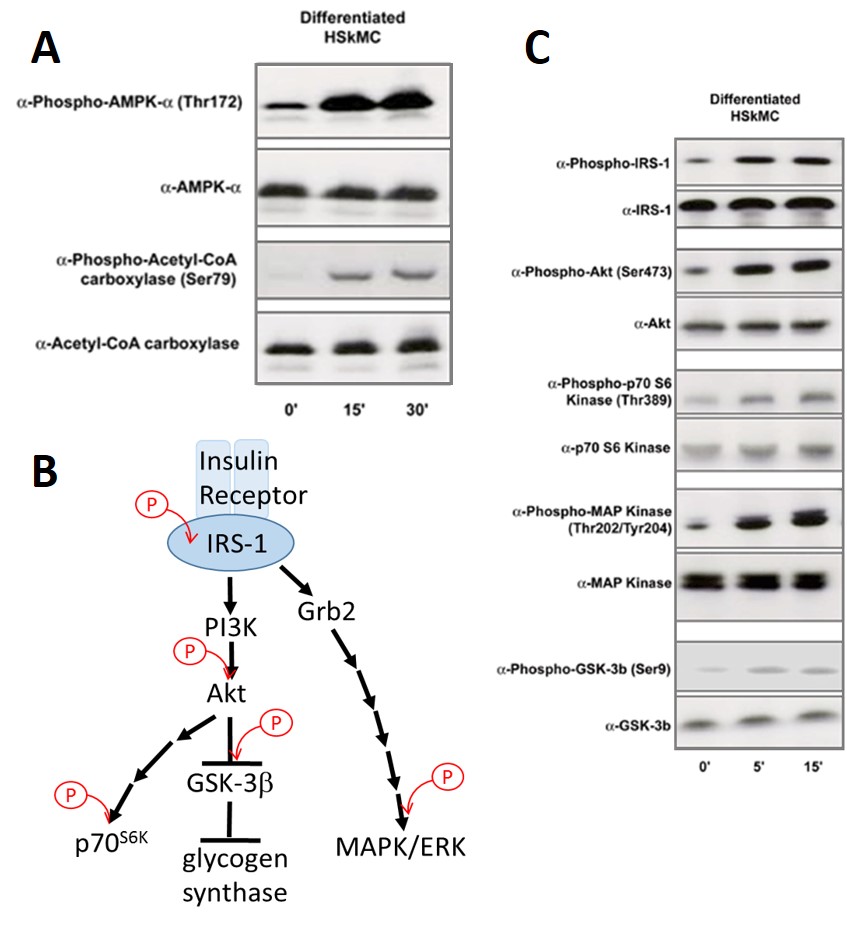
Human Skeletal Muscle Cells (HSkMC) response to forced activation of AMPK, leading to ACC phosphorylation. Cells serum-starved 16 hr & treated for 0, 15 or 30 min w/ 100nM oligomycin, which inhibits oxidative phosphorylation & causes activation of AMPK (A). Simplified insulin signal transduction map. Specific phosphorylation events examined in Fig. C are marke
...Human Skeletal Muscle Cells: S-HSkMC: Pre-Screened
Description
Human Skeletal Muscle Cells: S-HSkMC Pre-Screened for Insulin & AMPK signaling are isolated from the skeletal muscle of hamstrings and retain morphological, biochemical, and metabolic characteristics of skeletal muscle. Pre-screened HSkMCs can undergo differentiation to exhibit actin and myosin myofilaments and are specially tested for functional AMPK & Insulin Signaling Pathways.
AMPK Signaling Pathway
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a major cellular regulator of lipid and glucose metabolism and mediates the metabolic changes associated with exercise. AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits activity of acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACC), the enzyme responsible for making malonyl-CoA which is required for fatty acid chain elongation.
Insulin Signaling Pathway
Skeletal muscle is one of major target tissue of insulin action. Upon insulin binding, insulin receptor tyrosine kinases catalyze autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues providing docking sites for downstream signaling components, such as IRS-1 and Grb2, which relay the signaling further into the cell (see Fig.B).
Details
| Tissue | Normal healthy human limb skeletal muscle | |
|---|---|---|
| QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma, virus | |
| Cryovial | 500,000 HSkMC (2nd passage) frozen in Basal Medium w/ 10% FBS, 10% DMSO | |
| Kit | Cryovial frozen HSkMC (150-05f), Growth Medium (151-500), Subcltr Rgnt Kit (090K) | |
| Proliferating | Shipped in Gr Med, 3rd psg (flasks or plates) | |
| Doublings | At least 15 | |
| Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Resources
FAQs
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Primary Cell FAQs