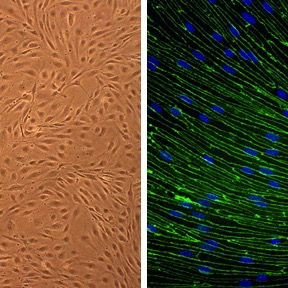
Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells: RBMVEC
Description
Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (RBMVEC) from Cell Applications, Inc. provide an excellent model system to study many aspects of endothelial function and disease, especially those related to the blood-brain barrier (BBB), including interactions between neurons, astorcytes and endothelial cells, brain cognitive function, search for therapeutic modulators, and develop novel drug delivery methods for crossing the BBB.
Says Binu Tharakan, Ph.D., F.A.H.A., Assistant Professor, Department of Surgery, Texas A&M Health Science Center:
“Our research focuses on the blood-brain barrier, brain edema and tight junction proteins, as well as mechanisms of brain microcirculation. We also examine microvascular permeability changes in traumatic and ischemic injuries. RBMVEC from Cell Applications factor heavily into our work and publications. We find the cells offer data reproducibility and a large number of population doublings, and also like to flexibility of multiple ordering formats.” RBMVEC from Cell Applications, Inc. have been utilized in a number of research publications, for example to:
- Serve as a gold standard control for endothelial markers VE-cadherin and CD31 expression
- Demonstrate a better brain penetration of cardiovascular and anti-stroke drugs Tanshinones IIA and IIB and Cryptotanshinone in the presence of PgP or MRP1/2 inhibitors or by using PEGylated gold nanoparticles
- Show that removal of excess glutamate from the blood by glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase correlates to a decrease in brain glutamate levels and confers neuroprotection against ischemic stroke
- Assess, along with Rat Astrocytes (RA) also obtained from Cell Applications, Inc., neuroprotective capabilities of bioenergy stabilizers in an in vitro model of stroke
- Show that bile acids cause activation of Rac1 and phosphorylation of occluding, explaining increased permeability of the blood brain barrier seen during obstructive cholestasis
- Demonstrate that saquinavir-associated dementia in HIV-positive patients is exacerbated by smoking due to the BBB disruptive effects of both nicotine and saquinavir, mediated by decrease in Notch-4 expression and increase in ROS
- Show that treatment with connexin43 mimetic peptide which transiently blocks gap junction function, reduces vascular leak and can be used to treat of central nervous system ischaemia
- Reveal that oxygen and glucose deprivation increase ROS, cytochrome c levels and caspase-3 activity, induce tight junction disruption and actin stress fiber formation, leading to BBB break down
- Investigate the interactions between neurons, astorcytes and endothelial cells by showing that exposure to metabolic stress induces tissue-type plasminogen activator release from neurons which induces AMPK activation, membrane recruitment of GLUT1, and GLUT1-mediated glucose uptake in astrocytes and endothelial cells, followed by the synthesis and release of lactic acid from astrocytes, and that the uptake of this lactic acid via the monocarboxylate transporter-2 promotes survival in neurons
- Study the proapoptotic and anti-angiogenic role of p75NTR in choroidal neovascularization
Details
| Tissue | Normal healthy brain from adult rat | |
|---|---|---|
| QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma | |
| Character | DiI-Ac-LDL uptake: Positive | |
| Bioassay | Attach, spread, proliferate in Growth Med | |
| Cryovial | 500,000 RBMVEC (2nd psg) frozen in Basal Medium w/ 10% FBS, 10% DMSO. | |
| Kit | Cryovial RBMVEC (R840-05a), Gr Med (R819-500), Attch Fctr Sln (123-100), Subcltr Rgnt Kit (090K) | |
| Proliferating | Shipped in Gr Med, 3rd psg (flasks or plates) | |
| Doublings | At least 10 | |
| Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Resources
FAQs
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Primary Cell FAQs