Human Dermal Lymphatic Microvascular Endothelial Cells: HDLMVEC
Description
Human Dermal Lymphatic Microvascular Endothelial (HDLMVEC) are isolated from lymphatic capillaries of normal human dermis. The lymphatic system interacts closely with the blood vascular system in maintaining tissue homeostasis. It plays a vital role in the body by regulating the immune system, transporting interstitial fluid, proteins and fat to the blood circulatory system. Lymphangiogenesis is also implicated in the metastatic process. Although lymphatic microvascular endothelial cells have many properties in common with blood microvascular endothelial cells, they also have unique functions due to their structural features. Lymphatic capillaries have thin and discontinuous base membranes, and lymphatic endothelial cells, unlike their blood vessel counterparts, are not as tightly connected with each other, rendering the capillaries highly permeable.
HDLMVEC, together with Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells, both from Cell Applications, Inc., have recently been used in a study demonstrating the key role of Prox1 and FOX C2 proteins in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma progression.
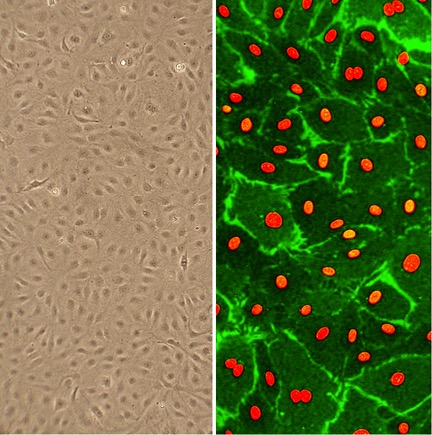
Characterization: They express VEGFR3, and respond to activation by VEGF-C (see Figure on left).
Details
| Tissue | Normal healthy human lymphatic capillaries from dermis | |
|---|---|---|
| QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma, virus | |
| Character | Factor VIII-related Ag, CD31 (PECAM-1), DiI-Ac-LDL uptake | |
| Bioassay | Attach, spread, proliferate in Growth Med (AFS-coated surface) | |
| Cryovial | 500,000 HDLMVEC (3rd psg) frozen in Basal Medium w/ 10% FB, 10% DMSO | |
| Kit | Cryovial of HDLMVEC (100L-05a), Gr Med (111-500), Attchmnt Fctr Soln (123-100), Subcltr Rgnt Kit (090K) | |
| Proliferating | Shipped in Tsfr Med, 4th psg (flasks or plates) | |
| Doublings | At least 12 | |
| Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Resources
FAQs
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Primary Cell FAQs