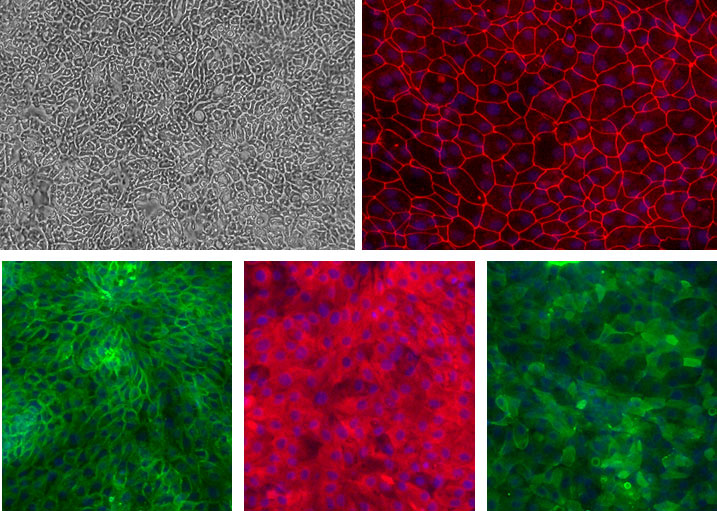
Human Duodenum Epithelial Cells (HDuEpC) and other Adult GI EpC monolayers.
Top left: Phase contrast of Ileum EpC. Top right (Red): ZO-1 of Duedenum EpC. Bottom left (Green): Na+/K+ ATPase of Colon EpC. Bottom middle (Red): pan-Cytokeratin of Gastric EpC. Bottom right (Green) Villin of Jejunum EpC. Blue: DAPI.
Human Duodenum Epithelial Cells: HDuEpC
Description
The intestinal epithelium is a single layer of cells organized into crypts and villi, known as the most rapidly self-renewing tissue in adult mammals. The cells that line the intestinal lumen perform the primary functions of digestion, water and nutrient absorption, and forms a barrier against luminal pathogens. Transit-amplifying cells spend approximately two days in the intestinal crypts, dividing 4–5 times before terminally differentiating into specialized intestinal epithelial cell types. In the small intestine, the surface area is dramatically enlarged through epithelial protrusions called villi. Three days after their terminal differentiation, the cells reach the tip of the villus, undergo spontaneous apoptosis, and are shed into the gut lumen. CAI’s intestinal epithelial culture system provides outstanding resource for investigation of intestinal epithelial cell physiology related to GI infection, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and intestinal cancer. Our epithelial cell culture system can be efficiently used as a test platform for the potential drug candidates and disease modulators. Other applications of this culture system include functional analysis of intestinal epithelium, GI disease modeling, and regenerative therapy preclinical testing such as drug compound screening and other validation assays. With optimized, defined culture media from CAI, the Intestinal Epithelial Cells can be seeded and maintained for as long as 8 days. Epithelial Cells grown in CAI medium form a monolayer of polarized epithelial cells with tight junction formation as evidenced by Villin (apical marker), Na+/K+ ATPase (basolateral marker), ZO-1 (tight junction marker) and pan-Cytokeratin (epithelial marker) staining.
Details
| Tissue | Normal healthy human duodenum. | |
|---|---|---|
| QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma, virus. | |
| Bioassay | Attach, spread, in Culture Medium. | |
| Cryovial | 500,000 or 1,000,000 HDuEpC in Freezing Medium. | |
| Kit | Cryovial frozen HDuEpC (732Du-05a, 732Du-10a), Culture Med (716DC-50), Coating Solution (1024-05), Thawing Solution (716T-20). | |
| Cultured | Shipped in flasks or plates in medium. | |
| Doublings | Cells do not divide and cannot be passaged. | |
| Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Resources
FAQs
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Primary Cell FAQs