Rat Astrocytes: RA
Description
Rat astrocytes (RA) are derived from rat cerebral cortex. Astrocytes are the most abundant cells in the central nervous system where they perform many functions, such as providing mechanical support and nutrients to neurons and removal of wastes from neurons; providing signaling to endothelial cells; regulating neurogenesis and controlling synaptic function. As the recognition of the importance of astrocytes in nervous system is increasing, RA serve as a useful in vitro model for exploring the diversity of astrocytes functions.
RA from CAI have been used to:
- Assess neuroprotective capabilities of bioenergy stabilizers in an in vitro model of stroke
- Investigate the effects of astrocytes on brain microvascular endothelial cells in relation to iron transport pathway
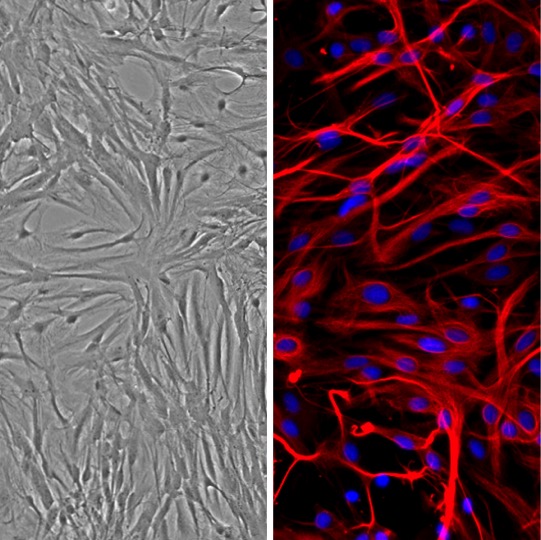
Characterization: Stained positive for GFAP (Example image at right shows neonatal Rat Astrocytes:RAn stained positive for glial fibrillary acidic protein)
Details
| Tissue | Normal healthy Rat brain | |
|---|---|---|
| QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma | |
| Cryovial | 500,000 RA (2nd passage) frozen in Basal Medium w/10% FBS, 10% DMSO | |
| Character | Positive for GFAP | |
| Bioassay | Attach, spread, proliferate in Growth Medium | |
| Kit | Cryovial frozen RA (R882A-05n), Growth Med (R821-500), Subcltr Rgnt Kit (090K) | |
| Proliferating | Shipped in Gr Med, 3rd psg (flasks or plates) | |
| Doublings | At least 10 | |
| Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Resources
FAQs
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Primary Cell FAQs