Human Coronary Artery Smooth Muscle Cells: Asthma: HCASMC-AS
Description
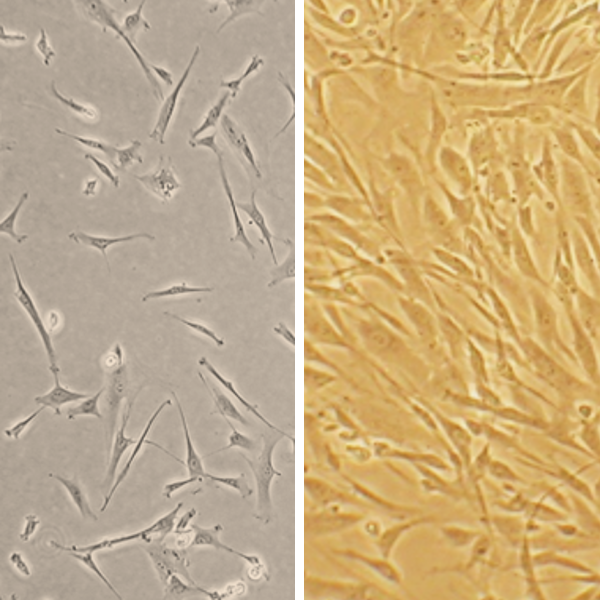
Human Coronary Artery Smooth Muscle Cells (HCASMC) provide an excellent model system to study all aspects of cardiovascular function and disease, especially those related to mechanisms of hyperplasia and hypertrophy of intimal smooth muscle cells leading to vascular occlusion in atherosclerosis and stent restenosis.
HCASMC from Cell Applications, Inc. have been utilized in a number of research studies, for example, to:
- Study signaling pathways regulating smooth muscle differentiation and chronic inflammation of arterial wall that leads to artherosclerosis
- Demonstrate that STAT-1 and STAT-3 regulate VEGF production in smooth muscle cells by having opposing effects on HIF-1α expression
- Examine the mechanisms of hypoxia and reoxigenation injuries in by demonstrating increased production of ROS and inflammatory cytokines, and further showing that DHA is not beneficial in this type of injuries
- Investigate (by also using human Internal Thoracic Artery Smooth Muscle Cells obtained from Cell Applications, Inc.), the gene expression differences between smooth muscle cells from different arteries, underlying their differential response to injuries and proliferation stimuli
- Suggest the hypermethylation of SOCS3 gene as the connection between TNF-α and IGF-1 released in response to mechanical injury during coronary intervention, and the induction of cytokines leading to intimal hyperplasia and restenosis
- Develop a novel VEGFR/MET-targeted inhibitor with improved antitumor efficacy and decreased toxicity
- Investigate novel therapies and drug combinations to achieve optimal target selectivity
- Generate elastic scaffolds for tissue engineering and novel treatment strategies to prevent stent restenosis by designing new materials, or drug therapies to preferentially inhibit smooth muscle cell growth
Characterization: positive for smooth muscle cell specific alpha-actin expression
Cell Applications offers a wide panel of cells for use in asthma research and airway drug development, such as Bronchial & Tracheal Epithelial Cells, Pulmonary & Lung Microvascular Endothelial cells and others. Multiple donor profiles and lots are available. Asthma (AS) is a chronic disease that inflames and narrows air passageways in the lungs. This airflow obstruction, which can flare up at any time, causes shortness of breath and can be life-threating in severe cases. Asthma often starts during childhood, and while there’s no cure, scientists and pharmaceutical companies have made strides in understanding, treating and managing the disease.
Details
| Tissue | Human coronary artery from donor with Asthma | |
|---|---|---|
| QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma, virus | |
| Character | Smooth muscle specific α-actin positive | |
| Bioassay | Attach, spread, proliferate in Growth Med | |
| Cryovial | 500,000 HCASMC-AS (2nd passage) frozen in Basal Medium w/ 10% FBS, 10% DMSO | |
| Kit | Cryovial frozen HCASMC-AS (350AS-05a), Growth Medium (311-500), Subcltr Rgnt Kit (090K) | |
| Proliferating | Shipped in Gr Med, 3rd psg (flasks or plates) | |
| Doublings | At least 16 | |
| Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
FAQs
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Primary Cell FAQs