Rat Cortical Neurons: RCoN
Description
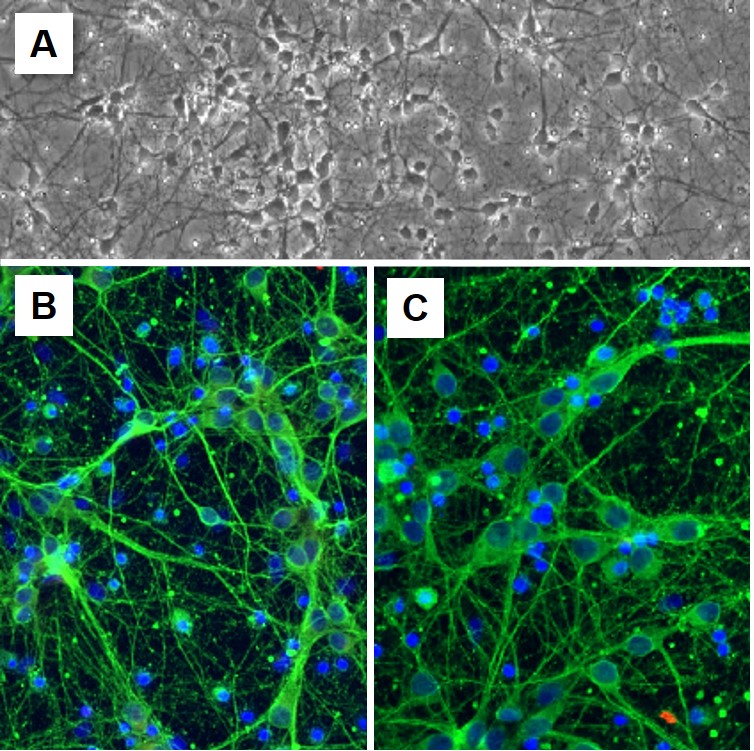
Rat cortical neurons (RCoN) are derived from cerebral cortices of day 18 embryonic Sprague Dawley rat brains. When cultured under the recommended conditions, RCoN arborize and form complex neurite network in one week. RCoN Stain positive for β III-Tubulin.
The cerebral cortex plays a key role in cognition, memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language and consciousness. Neurons connect to other neural cells through neurites and synapses to form complex neurocircuitry for signal transmission. A healthy circuitry in the brain is essential for cognitive functions, proper control and regulation of the other parts of the body. Dysfunction and degeneration in the cerebral cortex have been implicated in various brain injuries, neurological and psychiatric disorders. Cortical neurons, therefore, provide an excellent cellular model system to study disease mechanisms and pathophysiologies. They also serve as a platform for drug screening and development, toxicity tests, immunostaining, live cell imaging, co-culturing and electrophysiology.
Details
| Tissue | Normal healthy rat brain cortex | |
|---|---|---|
| QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma | |
| Character | Positive for β-III Tubulin | |
| Bioassay | Plate on Poly-D-Lysine coated surface, arborize to form neurite network in Culture Med | |
| Cryovial | 2M RCoN cryopreserved after isolation in Serum-Free Freezing Medium (042-50) | |
| Kit (2M) | 2M cryopreserved RCoN (R882N-20), Coating Soln I (027-05), Plating Med (R817P-10), Culture Med (R817-100) | |
| Doublings | N/A – Neurons don’t proliferate in vitro | |
| Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Resources
FAQs
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Primary Cell FAQs