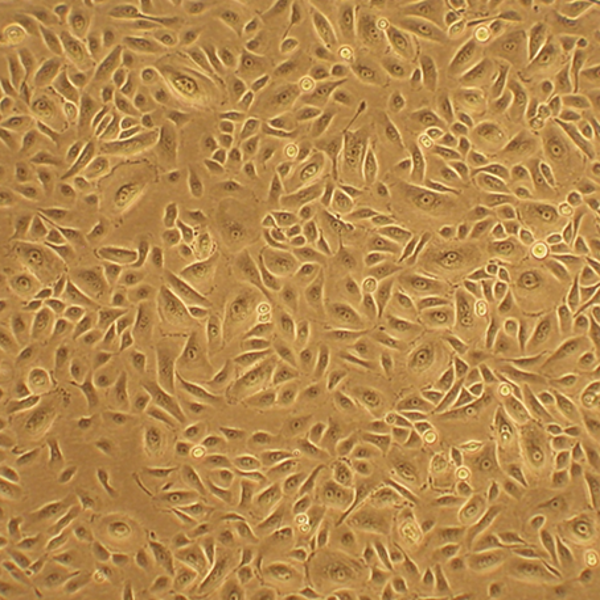
Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells: COPD: HBEpC-COPD
Description
Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (HBEpC) provide an excellent model system to study all aspects of epithelial function and disease, particularly those related to airway viral infections, as well as tissue repair mechanisms, signaling changes and potential treatments relevant to lung injuries, mechanical and oxidative stress, inflammation, pulmonary diseases and smoking. When grown on inserts and provided with the liquid/air interface, HBEpC can differentiate into a pseudostriated epithelium and serve as a more physiological 3D tissue model for in vitro studies. The HBEpC shown here were cultured (L) and immunolabeled for cytokeratin 18 (R). 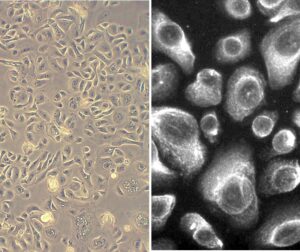
- Activation, expression and production of genes, kinases and signaling pathways by cytokines, growth factors, interleukins, binding proteins and pro-inflammatory molecules.
- Stimulation-dependent, observable changes in proliferation, bronchial epithelial permeability, crosslinking of membrane glycoproteins and cell surface adhesion molecules. Drug discovery cell screening for in vitro assay of compounds, or to extend and confirm high-throughput work done in cell lines.
- Clinical focused discoveries leveraging HBEpC include therapeutics to suppress tumor gene transcription, apoptosis, inflammation, auto-immune disease and viral infection, while enhancing cell protection, repair and lifespan.
Details
| Tissue | Human bronchial epithelium: COPD | |
|---|---|---|
| QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma, virus | |
| Bioassay | Attach, spread, proliferate in Growth Med | |
| Cryovial | 500,000 HBEpC-COPD (1st passage) frozen in Basal Med w/ 10% FBS, 10% DMSO | |
| Kit | Cryovial frozen HBEpC-COPD (502COPD-05a), Gr Med (511-500), Subculture Rgnt Kit (090K) | |
| Proliferating | Shipped in Gr Med, 3rd psg (flasks or plates) | |
| Doublings | At least 16 | |
| Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Resources
FAQs
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Primary Cell FAQs