Product Sheet CA11005
Description
BACKGROUND The bridging integrator-1 (BIN1) protein, also called Amphiphysin 2, is a member of BAR domain superfamily. BIN1 is a ubiquitous endocytic adaptor protein which was initially identified as a c-MYC-interacting pro-apoptotic tumor suppressor. Reduction of BIN1 expression in breast and other cancers was demonstrated, and introduction of BIN1 into tumor cells lacking endogenous expression reduced their proliferative capacity. Several splice variants of BIN1 harbor a MYC-binding domain (MBD), thus retaining the ability to physically interact with and inhibit the oncogenic functions of c-MYC. The BIN1–c-MYC interaction mediates c-MYC-induced apoptosis, at least partly. Interestingly, BIN1-induced cell death is not compromised by dysfunctional p53, caspase inhibition, and/or overexpression of BCL-2, which suggests that BIN1’s proapoptotic property could be useful for the eradication of cancer cells where p53 and/or caspases are frequently dysfunctional. It was demonstrated that BIN1 is a downstream mediator of E2F1-dependent apoptosis.1
On the other hand, The BAR domain superfamily proteins are involved in endocytosis, organelle biogenesis, cell division, and cell migration. As a member of the BAR domain superfamily, BIN1 was shown to induce membrane invagination and initiate tubulogenesis in skeletal muscle cells. BIN1 functions as a tubulogenesis membrane scaffolding protein. BIN1 deforms the membrane bilayer through interaction between its N-terminal positively charged BAR domain and acidic phospholipids within the cell membrane. Knowledge of the role of BIN1 in muscle cells includes evidence of BIN1 distribution on T-tubules of skeletal myocytes and that constitutive knockdown of BIN1 in mice is perinatal lethal, with pathology revealing a hypertrophic dilated cardiomyopathy. Indeed, BIN1 is involved in helping recruit Cav1.2 to T-tubules and acts as a kind of molecular landing pad for Cav1.2 delivery along microtubules. Thus, BIN1 plays a dual role in cardiac muscle cells; not only is it needed to help generate T-tubules, but it also designates T-tubules as the appropriate site for delivery of L-type calcium channels.2 Furthermore, other tissue-specific splice isoforms of BIN1 have been described to participate in specific biological processes, e.g. a neuronal isoform implicated in synaptic vesicle endocytosis.3
On the other hand, The BAR domain superfamily proteins are involved in endocytosis, organelle biogenesis, cell division, and cell migration. As a member of the BAR domain superfamily, BIN1 was shown to induce membrane invagination and initiate tubulogenesis in skeletal muscle cells. BIN1 functions as a tubulogenesis membrane scaffolding protein. BIN1 deforms the membrane bilayer through interaction between its N-terminal positively charged BAR domain and acidic phospholipids within the cell membrane. Knowledge of the role of BIN1 in muscle cells includes evidence of BIN1 distribution on T-tubules of skeletal myocytes and that constitutive knockdown of BIN1 in mice is perinatal lethal, with pathology revealing a hypertrophic dilated cardiomyopathy. Indeed, BIN1 is involved in helping recruit Cav1.2 to T-tubules and acts as a kind of molecular landing pad for Cav1.2 delivery along microtubules. Thus, BIN1 plays a dual role in cardiac muscle cells; not only is it needed to help generate T-tubules, but it also designates T-tubules as the appropriate site for delivery of L-type calcium channels.2 Furthermore, other tissue-specific splice isoforms of BIN1 have been described to participate in specific biological processes, e.g. a neuronal isoform implicated in synaptic vesicle endocytosis.3
REFERENCES
1. Cassimere, E.K. et al: Cell Death Diff. 16:1641-53, 2009
2. Hong, T.T. et al: PLoS ONE 8:e1000312, 2010
3. Wigge, P. & McMahon, H.T.: Trends Neurosci. 21:339-44, 1198
2. Hong, T.T. et al: PLoS ONE 8:e1000312, 2010
3. Wigge, P. & McMahon, H.T.: Trends Neurosci. 21:339-44, 1198
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
Cat.No.: | CA11005 |
Antigen: | Short peptide from human BIN1 sequence. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 - 1:200 ICC 1:50 - 1:200 FACS n/d |
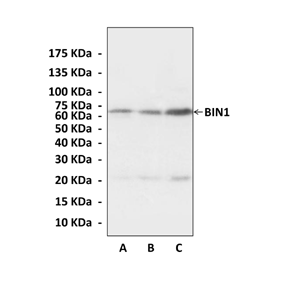
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 65 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of BIN1 proteins without cross-reactivity with other related proteins. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.