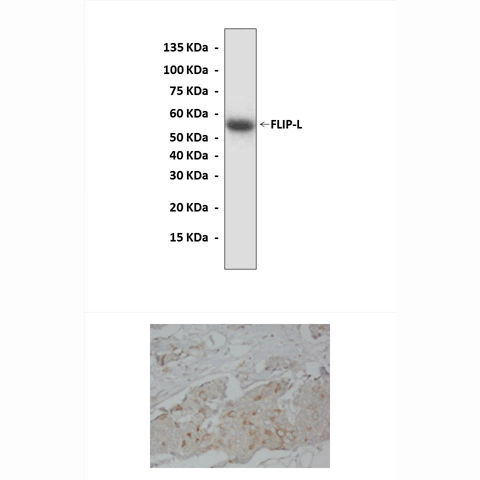
Description
BACKGROUND FLICE-inhibitory proteins (FLIP), an antagonist of death receptors (DRs), is an endogenous inhibitor of the Fas-associated death domain (FADD)/caspase-8 proapoptotic signaling pathway. Upon stimulation, CD95 (APO-1/Fas) recruits the adapter molecule FADD/MORT1, procaspase-8, and the cellular FLIP into the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). According to the induced proximity model, procaspase-8 is activated in the DISC in an autoproteolytic manner by two subsequent cleavage steps. FLIP proteins exist as a long (FLIP-L) and a short (FLIP-S) splice variant, both of them capable of protecting cells from death receptor-mediated apoptosis. FLIP-S contains only two tandem repeats of death effector domains and inhibits procaspase-8 activation in the DISC. In contrast, FLIP-L shares extensive homology with procaspase-8, with a C-terminal domain that is highly homologous to the procaspase-8 protease domain yet enzymatically inactive due to the lack of key active site residues.1 In addition, it was shown that FLIP-L directly interacts with Akt and FLIP-L overexpression interferes with Gsk3-beta phosphorylation levels. Furthermore, through its effects on Gsk3beta, FLIP-L overexpression in cancer cells induced resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). This effect was mediated by the regulation of p27Kip1 and caspase-3 expression.2
FLIP-L is a widely expressed molecule that confers resistance to DR-induced apoptosis in a wide range of cellular models. As an important modulator of caspase-8, FLIP-L regulates life and death in various types of normal cells and tissues. For instance, in T lymphocytes, FLIP-L interacts with different adaptor proteins to activate ERK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Thus, FLIP-L is a protein with dual roles displaying antiapoptotic or proliferation/differentiation properties, at least in the immune system. Moreover, FLIP-L is also a crucial factor in neurotrophin-induced control of neurite growth. It was shown that FLIP-L binds the neurotrophin receptor TrkA, but not p75NTR, during NGF stimulation.3 Overexpression of FLIP-L markedly increases neurotrophin-induced neurite outgrowth. In addition, FLIP-L renders resistance to death receptor-mediated apoptosis in many types of cancer cells. Dysregulation of c-FLIP expression has been shown to be associated with various diseases, such as cancer and autoimmune diseases, and c-FLIP might be a critical target for therapeutic intervention.4
FLIP-L is a widely expressed molecule that confers resistance to DR-induced apoptosis in a wide range of cellular models. As an important modulator of caspase-8, FLIP-L regulates life and death in various types of normal cells and tissues. For instance, in T lymphocytes, FLIP-L interacts with different adaptor proteins to activate ERK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Thus, FLIP-L is a protein with dual roles displaying antiapoptotic or proliferation/differentiation properties, at least in the immune system. Moreover, FLIP-L is also a crucial factor in neurotrophin-induced control of neurite growth. It was shown that FLIP-L binds the neurotrophin receptor TrkA, but not p75NTR, during NGF stimulation.3 Overexpression of FLIP-L markedly increases neurotrophin-induced neurite outgrowth. In addition, FLIP-L renders resistance to death receptor-mediated apoptosis in many types of cancer cells. Dysregulation of c-FLIP expression has been shown to be associated with various diseases, such as cancer and autoimmune diseases, and c-FLIP might be a critical target for therapeutic intervention.4
REFERENCES
1. Chang, D.W. et al: EMBO J. 21:3704-14, 2002
2. Quintavalle, C. et al: Cell Death Diff. 2010 (in press)
3. Moubarak, R.S. et al: J. Neurosci. 30:6094-105, 2010
4. Krueger, A. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 276:20633-4, 2001
2. Quintavalle, C. et al: Cell Death Diff. 2010 (in press)
3. Moubarak, R.S. et al: J. Neurosci. 30:6094-105, 2010
4. Krueger, A. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 276:20633-4, 2001
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
|
Cat.No.:
|
CA1034
|
|
Antigen:
|
Short peptide from human FLIP-L sequence.
|
|
Isotype:
|
Rabbit IgG
|
|
Species & predicted
species cross-
reactivity ( ):
|
Human
|
|
Applications &
Suggested starting
dilutions:*
|
WB 1:1000
IP n/d
IHC 1:50 - 1:200
ICC n/d
FACS n/d
|
|
Predicted Molecular
Weight of protein:
|
56 kDa
|
|
Specificity/Sensitivity:
|
Detects endogenous levels of FLIP-L proteins without cross-reactivity with other related proteins.
|
|
Storage:
|
Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.