Product Sheet CB4736
Description
BACKGROUND Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) acts as a potent mitogen, chemoattractant and survival factor for mesenchymal cells. In addition to its importance in mammalian development, PDGF plays a critical role in physiological repair mechanisms and in the pathogenesis of various proliferative diseases.1 The biological effects of PDGF are initiated via two related receptor tyrosine kinases, termed alpha and beta PDGF receptors. There are three PDGF isoforms, denoted PDGF-AA, -AB, and -BB, which are homo- or heterodimers of related A and B polypeptide chains. The PDGFR-beta binds only B-chain-containing PDGF isoforms, PDGF-BB binds with high affinity (ICd, 0.5 m) and PDGF-AB with lower affinity (Kd, 2.5 m), but there is no appreciable affinity for PDGF-AA. The alpha-receptor binds all three PDGF isoforms with similar affinities (Kd, 0.1-0.5 nM). The receptors are structurally related transmembrane glycoproteins and form, together with CSF-1 receptor, Flt3, and c-Kit, a subfamily within the superfamily of tyrosine kinases.2 Binding of PDGF induces dimerization of the receptors in vitro and in vivo. PDGF-AA induces PDGFR alpha-alpha homodimers, PDGF-AB induces PDGFR alpha-alpha homodimers and alpha-beta heterodimers, and PDGF-BB induces all three types (alpha-alpha, alpha-beta, and beta- beta) of dimers. Dimerization is accompanied by, and might be a prerequisite for activation of the kinase. Kinase activation is visualized as tyrosine phosphorylation of the receptor molecules, known as autophosphorylation. Tyrosine phosphorylation sites in PDGFR, as with other RTKs, serve two purposes: (i) to control the state of activity of the kinase and (ii) to create binding site for downstream signal transduction molecules, which in many cases also are substrates for the kinase.3 The activities of the signaling components are ultimately manifested as specific biological responses.
REFERENCES
1. Fredriksson, L et al.: Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:197, 2004
2 Tallquist, M. & Kazlauskas, A.: Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:205, 2004
3. Funa, K. & Uramoto, H.: Acta Biochim Pol. 50:647, 2003
2 Tallquist, M. & Kazlauskas, A.: Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:205, 2004
3. Funa, K. & Uramoto, H.: Acta Biochim Pol. 50:647, 2003
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
Cat.No.: | CB4736 |
Antigen: | E. coli-expressed cytoplasmic domain of human PDGF receptor-beta. |
Isotype: | Rabbit Polyclonal IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC (Paraffin) n/d ICC n/d FACS n/d |
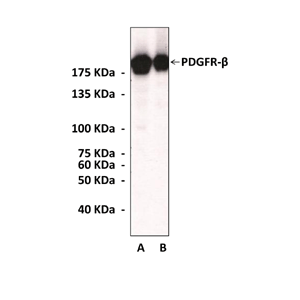
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 190 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Anti-PDGFR-beta specifically detects endogenous levels of PDGF receptor-beta. This antibody does not cross-react with other PDGFR-family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyclonal PDGFR-Beta Antibody: Polyclonal PDGFR-beta Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CB4736 | Price: $302.00 |