Product Sheet CA1322
Description
BACKGROUND Plasma ultrafiltration during a primary urine formation in the glomerulus is a central function of the kidneys. This process is associated with the anatomical region of the kidney, which is composed of a basement membrane with highly specialized epithelial cells called podocytes. As a part of the glomerular filtration barrier, the slict diagram (SD) is thought to function as a filter that is size-selective. In the nephrotic syndrome, the normal podocyte substructure is lost; the effacement of podocyte foot processes results in a massive proteinuria. NPHS2 was identified by positional cloning to be the target gene of autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome, which is characterized by early childhood onset of proteinuria, rapid progression to end-stage renal disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.1 NPHS2 encodes for Podocin, a protein exclusively expressed in podocytes of the developing and mature glomeruli. Podocin plays a critical role in the function of the glomerular filtration barrier. Podocin is a member of the stomatin protein family with a short N-terminal domain, a transmembrane region, and a cytosolic C-terminal domain. Podocin is predicted to form a membrane-associated hairpin-like structure with a cytosolic N- and C-terminal domain that is typical for stomatin-like proteins and caveolins. In podocytes, Podocin localized at the insertion site of the SD complex in the podocyte foot processes. Furthermore, it is a constituent of detergent-insoluble microdomains and has been shown to interact with another raft-associated podocyte proteins, CD2-associated protein (CD2AP) and nephrin. Hence, Podocin may act as a scaffolding protein in the podocyte lipid rafts, recruiting nephrin and CD2AP to these microdomains. It is known that nephrin forms zipper-like interactions to maintain the structure of podocyte foot processes. Nephrin is a signaling molecule, which stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinases. Moreover, it was shown that nephrin-induced signaling is greatly enhanced by Podocin, which binds to the cytoplasmic tail of nephrin. Mutational analysis suggests that abnormal or inefficient signaling through the nephrin-Podocin complex contributes to the development of podocyte dysfunction and proteinuria.2 In addition CIN85/RukL may regulate interaction of CD2AP, nephrin and Podocin. Podocin endocytosis was mediiated via CIN85/RukL-mediated ubiquitination.3
REFERENCES
1. Boute, B. et al: Nature Genet. 24:349-54, 2000
2. Huber, T.B. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 276:41543-6, 2001
3. Tossidou, I. Et al: J. Biol. Chem. 285:25285-95, 2010
2. Huber, T.B. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 276:41543-6, 2001
3. Tossidou, I. Et al: J. Biol. Chem. 285:25285-95, 2010
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
Cat.No.: | CA1322 |
Antigen: | Short peptide from human Podocin sequence. |
Isotype: | Rabbit IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 - 1:200 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
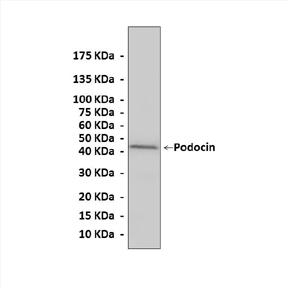
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 42 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of Podocin proteins without cross-reactivity with other related proteins. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbit Podocin Antibody: Rabbit Podocin Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CA1322 | Price: $375.00 |