Product Sheet CP10270
Description
BACKGROUND The Kelch-related proteins are a superfamily of proteins conserved in a wide range of organisms, from viruses to mammals. At least 60 Kelch-related proteins have been identified, but their physiological and biochemical functions remain largely uncharacterized. Rearrangement of the actin-based cytoskeleton is regulated by a large number of actin-binding proteins. The kelch-related proteins are believed to be important for the maintenance of the ordered cytoskeleton. The Drosophila Kelch proteins colocalize with actin filaments in a structure called the ring canal, which bridges 15 nurse cells and the oocyte. Drosophila Kelch protein plays an important role in maintaining actin organization during the development of ring canals. The Kelch-related proteins have diverse functions in cell morphology, cell organization, and gene expression, and function in multiprotein complexes through contact sites in their β-propeller domains. Recently, a new member of the BTB/Kelch repeat family, gigaxonin, was reported to be a pathological target for neurodegenerative disorders in which alterations were found to contain multiple mutations in the Kelch repeats in the neurofilament network. Alterations and mutations of these proteins were found in brain tumors and neurodegenerative disorders.1
The actin-binding protein Kelch-like 22 (KLHL22) a 634 amino acid protein that belongs to the evolutionarily-conserved Kelch protein super-family. Human KLHL22 protein contains six kelch repeats and one BTB (POZ) domain. BTB/POZ domain are involved in protein-protein interactions. There are two isoforms of KLHL22 that are produced as a result of alternative splicing events. It was shown that KLHL22 plays important role in regulation of mitosis. KLHL22 and KLH21 are associated with Cullin3, a E3 ubiqutin ligase. Cul3 (Cullin3) assembles with BTB domain adaptors, which bind to specific substrates via distinct protein interaction domains.2
The actin-binding protein Kelch-like 22 (KLHL22) a 634 amino acid protein that belongs to the evolutionarily-conserved Kelch protein super-family. Human KLHL22 protein contains six kelch repeats and one BTB (POZ) domain. BTB/POZ domain are involved in protein-protein interactions. There are two isoforms of KLHL22 that are produced as a result of alternative splicing events. It was shown that KLHL22 plays important role in regulation of mitosis. KLHL22 and KLH21 are associated with Cullin3, a E3 ubiqutin ligase. Cul3 (Cullin3) assembles with BTB domain adaptors, which bind to specific substrates via distinct protein interaction domains.2
REFERENCES
1. Seng, S. et al: Mol. Cell. Biol. 26:8371-84, 2006
2. Maerki, S. et al: J. Cell Biol. 187:791-800, 2009
2. Maerki, S. et al: J. Cell Biol. 187:791-800, 2009
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
Cat.No.: | CP10270 |
Antigen: | Purified recombinant human KLHL22 fragments expressed in E. coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC n/d ICC 1:50 - 1:200 FACS n/d |
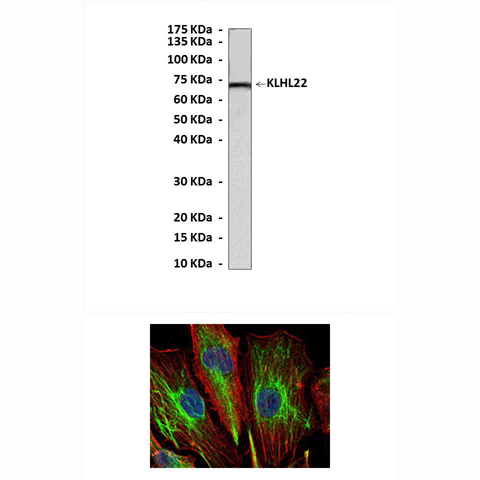
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 72 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects KLHL22 proteins without cross-reactivity with other related proteins. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse KLHL22 Antibody: Mouse KLHL22 Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CP10270 | Price: $413.00 |