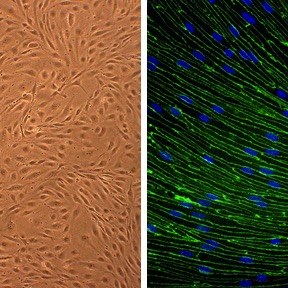
Instructions RBMVEC
5 Important Cell Culture Rules
MSDS Cryopreserved Cells
Cell Apps Flyer Nervous System
Cell Apps Flyer Brain Cells
Cell Apps Fllyer Cardiovascular Cells
Cell Apps Flyer Endothelial Cells
Cell Apps Poster Primary Cells
Cell Applications Inc Brochure
Description
Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (RBMVEC) from Cell Applications, Inc. provide an excellent model system to study many aspects of endothelial function and disease, especially those related to the blood-brain barrier (BBB), including interactions between neurons, astorcytes and endothelial cells, brain cognitive function, search for therapeutic modulators, and develop novel drug delivery methods for crossing the BBB.
Says Binu Tharakan, Ph.D., F.A.H.A., Assistant Professor, Department of Surgery, Texas A&M Health Science Center:
“Our research focuses on the blood-brain barrier, brain edema and tight junction proteins, as well as mechanisms of brain microcirculation. We also examine microvascular permeability changes in traumatic and ischemic injuries. RBMVEC from Cell Applications factor heavily into our work and publications. We find the cells offer data reproducibility and a large number of population doublings, and also like to flexibility of multiple ordering formats.”
RBMVEC from Cell Applications, Inc. have been utilized in a number of research publications, for example to:
- Serve as a gold standard control for endothelial markers VE-cadherin and CD31 expression
- Demonstrate a better brain penetration of cardiovascular and anti-stroke drugs Tanshinones IIA and IIB and Cryptotanshinone in the presence of PgP or MRP1/2 inhibitors or by using PEGylated gold nanoparticles
- Show that removal of excess glutamate from the blood by glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase correlates to a decrease in brain glutamate levels and confers neuroprotection against ischemic stroke
- Assess, along with Rat Astrocytes (RA) also obtained from Cell Applications, Inc., neuroprotective capabilities of bioenergy stabilizers in an in vitro model of stroke
- Show that bile acids cause activation of Rac1 and phosphorylation of occluding, explaining increased permeability of the blood brain barrier seen during obstructive cholestasis
- Demonstrate that saquinavir-associated dementia in HIV-positive patients is exacerbated by smoking due to the BBB disruptive effects of both nicotine and saquinavir, mediated by decrease in Notch-4 expression and increase in ROS
- Show that treatment with connexin43 mimetic peptide which transiently blocks gap junction function, reduces vascular leak and can be used to treat of central nervous system ischaemia
- Reveal that oxygen and glucose deprivation increase ROS, cytochrome c levels and caspase-3 activity, induce tight junction disruption and actin stress fiber formation, leading to BBB break down
- Investigate the interactions between neurons, astorcytes and endothelial cells by showing that exposure to metabolic stress induces tissue-type plasminogen activator release from neurons which induces AMPK activation, membrane recruitment of GLUT1, and GLUT1-mediated glucose uptake in astrocytes and endothelial cells, followed by the synthesis and release of lactic acid from astrocytes, and that the uptake of this lactic acid via the monocarboxylate transporter-2 promotes survival in neurons
- Study the proapoptotic and anti-angiogenic role of p75NTR in choroidal neovascularization
Details
Tissue | Normal healthy brain from adult rat |
QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma |
Character | DiI-Ac-LDL uptake: Positive |
Bioassay | Attach, spread, proliferate in Growth Med |
Cryovial | 500,000 RBMVEC (2nd psg) frozen in Basal Medium w/ 10% FBS, 10% DMSO. |
Kit | Cryovial RBMVEC (R840-05a), Gr Med (R819-500), Attch Fctr Sln (123-100), Subcltr Rgnt Kit (090K) |
Proliferating | Shipped in Gr Med, 3rd psg (flasks or plates) |
Doublings | At least 10 |
Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Total Kit, adult: 5x10^5 Cells (Adult), Medium & Subculture Reagents (See Details tab for specifics) | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: R840K-05a | Price: $1,052.00 | |
| Cryopreserved Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (RBMVEC), adult: Frozen RBMVEC (5x10^5) | Size: 1 Cryovial | CAT.#: R840-05a | Price: $845.00 | |
| Proliferating Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (RBMVEC), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: T-25 Flask | CAT.#: R841-25a | Price: $845.00 | |
| Proliferating Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (RBMVEC), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: T-75 Flask | CAT.#: R841-75a | Price: $1,035.00 | |
| Proliferating Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (RBMVEC), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: 24 Well | CAT.#: R841-24Wa | Price: $1,035.00 |
Related Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rat Brain EC Growth Medium: All-in-one ready-to-use | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: R819-500 | Price: $148.00 | |
| Rat Brain EC Growth Medium Kit: Basal medium & growth supplement sold together packaged separately | Size: Yields 500 ml | CAT.#: R819K-500 | Price: $159.00 | |
| Rat Brain EC Basal Medium: Basal medium (contains no growth supplement). Add GS before use. | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: R818-500 | Price: $84.00 | |
| Rat Brain EC Growth Supplement: Added to Basal Medium to create Growth Medium | Size: 30 ml | CAT.#: R819-GS | Price: $105.00 | |
| Rat Brain EC Basal Medium wo Phenol Red: Basal medium (contains no growth supplement). Add GS before use. Without Phenol Red. | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: R818PR-500 | Price: $86.00 | |
| Rat Brain EC Growth Medium wo Hydrocortisone: All-in-one ready-to-use, without Hydrocortisone | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: R819H-500 | Price: $171.00 | |
| Rat Brain EC Growth Medium wo Phenol Red: All-in-one ready-to-use, without Phenol Red | Size: 500 | CAT.#: R819PR-500 | Price: $171.00 |
Extended Family Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freezing Medium: For general cryopreservation of most primary cells. Contains FBS & DMSO. | Size: 50 ml | CAT.#: 040-50 | Price: $54.00 | |
| Cytofect Endothelial Cell Transfection Kit (250 x 24-Wells): 250 x 24-Well Rxns | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: TF101K | Price: $546.00 | |
| Cytofect Endothelial Cell Transfection Sample Kit (25 x 24-Wells): 25 x 24-Well Rxns | Size: 1 Sample Kit | CAT.#: TF101KS | Price: $68.00 | |
| Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell RNA (RBMVEC RNA), Adult: Total RNA prepared from Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: R840-R10a | Price: $598.00 | |
| Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell RNA (RBMVEC RNA), Adult: Total RNA prepared from Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: R840-R25a | Price: $1,197.00 | |
| Subculture Reagent Kit: 100 ml each of HBSS, Trypsin/EDTA & Trypsin Neutralizing Solution | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: 090K | Price: $69.00 |
Resources/Documents
Citations
Publications
2017
Gray, S.M., Aylor, K.W. and Barrett, E.J., 2017. Unravelling the regulation of insulin transport across the brain endothelial cell. Diabetologia, pp.1-10.
2016
Alluri, H., M. Grimsley, C. Shaji, K. Varghese, S. Zhang, C. Peddaboina, B. Robinson, M. Beeram, J. Huang and B. Tharakan. 2016. Attenuation of Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown and Hyperpermeability by Calpain Inhibition. J Biol Chem, jbc.M116.735365.
Alluri, H., R. Wilson, C. Shaji, K. Wiggins-Dohlvik, S. Patel, Y. Liu, X. Peng, M. Beeram, M. Davis, J. Huang and B. Tharakan. 2016. Melatonin Preserves Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity and Permeability via Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Inhibition. PLoS ONE 11(5): e0154427.
Meijer, R, S. Gray, K. Aylor and E. Barrett. 2016. Pathways for insulin access to the brain: the role of the microvascular endothelial cell. Am J Physiol – Heart & Circ Physiol, 311:H1132-H1138.
Patel, C., Z. Xu, E. Shosha, J. Xing, R. Lucas, R. Caldwell, R. Caldwell and S. Narayanan. 2016. Treatment with polyamine oxidase inhibitor reduces microglial activation and limits vascular injury in ischemic retinopathy. BBA Molec Basis of Disease, 9:1628-1639.
Zhou, T., J. Rivera, V. Bhosle, I. Lahaie, Z. Shao, H. Tahiri, T. Zhu, A. Plosa, A. Dorfman, A. Beaudry-Richard, S. Costantino, G. Lodygensky, P. Lachapelle and S. Chemtob. 2016. Choroidal Involution Is Associated with a Progressive Degeneration of the Outer Retinal Function in a Model of Retinopathy of Prematurity: Early Role for IL-1β. Am J Pathol, 186:3100-3116.
2015
Altmann, J., G. Yan, J. Meeks, M. Abood, E. Brailoiu, and G. Brailoiu. 2015.G protein-coupled estrogen receptor-mediated effects on cytosolic calcium and nanomechanics in brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Neurochem, online: 2 MAR. DOI: 10.1111/jnc.13066.
Anand, P., A. O’Neil, E. Lin, T. Douglas, and M. Holford. 2015. Tailored delivery of analgesic ziconotide across a blood brain barrier model using viral nanocontainers. Nature, Scientific Reports, 5: Article 12497, doi:10.1038/srep12497.
Brailoiu, G., E. Deliu, L. Bram, J. Soboloff, M. Abood, E. Unterwald, and E. Brailoiu. 2015. Cocaine Inhibits Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells: Critical Role for Sigma-1 Receptors. Biochem J, DOI: 10.1042/BJ20150934.
Deosarkar, S., B. Prabhakarpandian, B. Wang, J. Sheffield, B. Krynska and M. Kiani. 2015. A Novel Dynamic Neonatal Blood-Brain Barrier on a Chip. PLoS ONE 10(11): e0142725.
Sitaras, N., J. Rivera, B. Noueihed, M. Bien-Aime, K. Zaniolo, S. Omri, D. Hamel, T. Zhu, P. Hardy, P. Sapieha, J. Joyal, and S. Chemtob. 2015. Retinal Neurons Curb Inflammation and Enhance Revascularization in Ischemic Retinopathies via Proteinase-Activated Receptor-2. The American Journal of Pathology, 185:581-595.
Zarebkohan, A., F. Najafi, H. Moghimi, M. Hemmati, M. Deevband, and B. Kazemi. 2015. Synthesis and characterization of a PAMAM dendrimer nanocarrier functionalized by SRL peptide for targeted gene delivery to the brain. Eu J Pharm Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2015.06.024.
2014
Alluri, H., H. Stagg, R. Wilson, R. Clayton, D. Sawant, M. Koneru, M. Beeram, M. Davis, and B. Tharakan. 2014. Reactive Oxygen Species-Caspase-3 Relationship in Mediating Blood–Brain Barrier Endothelial Cell Hyperpermeability Following Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation and Reoxygenation. Microcirculation, 21:187-195.
An, J., W. Haile, F. Wu, E. Torre, and M. Yepes. 2014. Tissue-type plasminogen activator mediates neuroglial coupling in the central nervous system. Neuroscience, 257:41-48.
Camós, S., C. Gubern, M. Sobrado, R. Rodriguez, V. Romera, M. Moro, I. Lizasoain, J. Serena, J. Mallolas and M. Castellanos. 2014. The high-mobility group I-Y transcription factor is involved in cerebral ischemia and modulates the expression of angiogenic proteins. Neuroscience, 269:112-130.
Carver, K., D. Lourim, A. Tryba and D. Harder. 2014. Rhythmic expression of cytochrome P450 epoxygenases CYP4x1 and CYP2c11 in the rat brain and vasculature. Am J Physiol – Cell Physiol, 307:C989-C998.
Quinn, M., M. McMillin, C. Galindo, G. Frampton, H. Pae and S. DeMorrow. 2014. Bile acids permeabilize the blood brain barrier after bile duct ligation in rats via Rac1-dependent mechanisms. Digestive and Liver Disease, 46:527-534.
Schock, S., H. Edrissi, D. Burrger, R. Cadonic, A. Hakim, and C. Thompson. 2014. Microparticles generated during chronic cerebral ischemia deliver proapoptotic signals to cultured endothelial cells. BBRC, 450:912-917.
Wen, J., S. Qian, Q Yang, L. Deng, Y. Mo, and Y. Yu. 2014. Overexpression of netrin‑1 increases the expression of tight junction‑associated proteins, claudin‑5, occludin, and ZO‑1, following traumatic brain injury in rats. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 8:881-886.
Wiggins-Dohlvik, K., M. Merriman, C. Shaji, H. Alluri, M. Grimsley, M. Davis, R. Smith, and B. Tharakan. 2014. Tumor necrosis factor-α disruption of brain endothelial cell barrier is mediated through matrix metalloproteinase-9. The American Journal of Surgery, 208:954–960.
2013
Alluri, H., H.W. Stagg, R.L. Wilson, R.P. Clayton, D. Sawant, M. Koneru, M.R. Beeram, M.L. Davis, and B. Tharakan. 2013. Reactive Oxygen Species-Caspase-3 Relationship in Mediating Blood-Brain Barrier Endothelial Cell Hyperpermeability Following Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation and Reoxygenation. Microcirculation: DOI: 10.1111/micc.12110.
An, J., W.B. Haile, F. Wu, E. Torre, and M. Yepes. 2013. Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator Mediates Neuroglial Coupling in the Central Nervous System. Neuroscience. 257C:41-48.
Liu, S., G. Zhen, R.C. Li, and S. Dore. 2013. Acute bioenergetic intervention or pharmacological preconditioning protects neuron against ischemic injury. Journal of experimental stroke & translational medicine. 6:7-17.
Tahiri, H., C. Yang, F.o. Duhamel, S. Omri, E. Picard, S. Chemtob, and P. Hardy. 2013. p75 neurotrophin receptor participates in the choroidal antiangiogenic and apoptotic effects of T-lymphocyte-derived microparticles. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science. 54:6084-6092.
2012
DeCoster, M., J. McNamara, K. Cotton, D. Green, C. Jeyasankar, R. Idowu, K. Evans, Z. Xing, and Y. Lvov. Bionanocomposites for multidimensional Brain Cell signaling. Ch. 8. In Thomas, S., N. Ninan, S. Mohan, and E. Francis. 2012. Natural Polymers, Biopolymers, Biomaterials, Composites, Blends, and IPNS. Advances in Materials Science, Volume 2.
Danesh-Meyer, H.V., N.M. Kerr, J. Zhang, E.K. Eady, S.J. O'Carroll, L.F.B. Nicholson, C.S. Johnson, and C.R. Green. 2012. Connexin43 mimetic peptide reduces vascular leak and retinal ganglion cell death following retinal ischaemia. Brain. 135:506-520.
Etame, A. 2012. Enhanced Delivery of Gold Nanoparticles with Therapeutic Potential for Targeting Human Brain Tumors. PhD Dissertation, U Toronto.
2011
Campos, F., T. Sobrino, P. Ramos-Cabrer, B. Argibay, J. Agulla, M. Perez-Mato, R. Rodriguez-Gonzalez, D. Brea, and J. Castillo. 2011. Neuroprotection by glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase in ischemic stroke: an experimental study. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism. 31:1378-1386.
Etame, A.B., C.A. Smith, W.C.W. Chan, and J.T. Rutka. 2011. Design and potential application of PEGylated gold nanoparticles with size-dependent permeation through brain microvasculature. Nanomedicine. 7:992-1000.
Su, K.-H., S.-K. Shyue, Y.R. Kou, L.-C. Ching, A.-N. Chiang, Y.-B. Yu, C.-Y. Chen, C.-C. Pan, and T.-S. Lee. 2011. β Common receptor integrates the erythropoietin signaling in activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J. Cell. Physiology. 226:3330-3339.
2010
Manda, V., R. Mittapalli, W. Geldenhuys and P. Lockman. 2010. Chronic exposure to nicotine and saquinavir decreases endothelial Notch-4 expression and disrupts blood-brain barrier integrity. J Neurochem, 115:515-525.
2009
Johansson, Å., J. Lau, M. Sandberg, L.A.H. Borg, P.U. Magnusson, and P.O. Carlsson. 2009. Endothelial cell signalling supports pancreatic beta cell function in the rat. Diabetologia. 52:2385-2394.
Makino, A., J. Suarez, H. Wang, D. Belke, B. Scott, and W. Dillmann. 2009. Thyroid hormone receptor-β is associated with coronary angiogenesis during pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Endocrinology, 150:2008-2015.
2007
Yu, X, S. Lin, X, Chen, Z. Zhou, J Ling, W Duan, B. Chowbay, J. Wen, E. Chan, J. Cao, C. Li, and S. Zhou. 2007 Transport of Cryptotanshinone, a Major Active Triterpenoid in Salvia Miltiorrhiza Bunge Widely Used in the Treatment of Stroke and Alzheimer's Disease, Across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Current Drug Metabolism, 8:365-377.
Zhou, Z., X. Chen, J. Liang, X. Yu, J. Wen, and S. Zhou. 2007. Involvement of P-glycoprotein and Multidrug Resistance Associated Protein 1 in the Transport of Tanshinone IIB, a Primary Active Diterpenoid Quinone from the Roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza, Across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Drug Metabolism Letters, 1:205-217.