Instructions RCm
5 Important Cell Culture Rules
MSDS Cryopreserved Cells
Cell Apps Flyer Cardiovascular Cells
Cell Apps Poster Primary Cells
Cell Applications Inc Brochure
Description
RCm from Cell Applications, Inc. have been used to investigate mechanisms of mitochondrial and cardiovascular toxicity exhibited by anti-cancer drugs targeting angiogenesis. Antipsychotic drugs, thioridazine and mesoridazine, were shown to inhibit gap junction communication and affect the beating of RCm, explaining the cardiac side-effects observed in some patients. Clostridium difficile toxin B was shown to disrupt coordinated contractility and rhythmicity in RCm, but the damage was prevented by a caspase-3 inhibitor.
Additionally, RCm were used to demonstrate that Mas receptor, a GPCR activates phospholipase C and causes inositol phosphate accumulation, contributing to cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. The same system was then used to screen for agonists and inverse agonists for Mas. Inhibiting Mas function provided cardioprotective effects in mice and in isolated rat hearts. RCm were also used to develop a new probe for positron emission tomography that allows for more effective cardiac imaging.
***FOR SHIPMENT THE FOLLOWING MONDAY, PLEASE PLACE RCm ORDERS BY TUESDAY 12pm PST the week prior.***
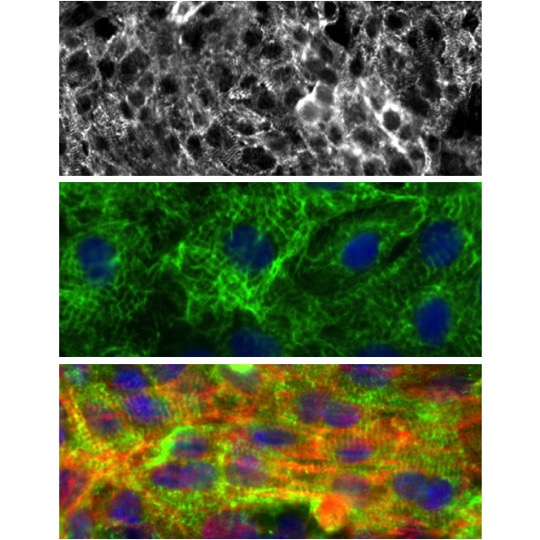
(Click to Enlarge) Top: Rat Cardiomyocytes (RCm) immunolabeled for desmin, large field of view showing nearly 100% desmin-positive cardiomyocytes, 20x. Middle: RCm stained for desmin. Bottom: Detailed view of desmin (green) and actin (red) striations within RCm; nuclei stained with DAPI (blue), 40x.
Details
Tissue | Normal healthy neonatal rat heart |
QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma |
Bioassay | Attaches on FBS-coated culture ware, Remains viable 2-4 days in Cltr Med |
Cryovial | N/A |
Kit | N/A |
Cultured | Shipped w/in 3 days after plating in Maint Med (flasks or plates) |
Doublings | N/A |
Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultured RCm: Fresh, Plated Cells in Maintenance Medium | Size: 3 of T-25 Flasks | CAT.#: R357-25-3 | Price: $1,533.00 | |
| Cultured RCm: Fresh, Plated Cells in Maintenance Medium | Size: 2 of T-75 Flask | CAT.#: R357-75-2 | Price: $1,506.00 | |
| Cultured RCm: Fresh, Plated Cells in Maintenance Medium | Size: 2 of 12-Well Multiwell | CAT.#: R357-12W-2 | Price: $1,550.00 | |
| Cultured RCm: Fresh, Plated Cells in Maintenance Medium | Size: 2 of 24-Well Multiwell | CAT.#: R357-24W-2 | Price: $1,657.00 | |
| Cultured RCm: Fresh, Plated Cells in Maintenance Medium | Size: 2 of 48-Well Multiwell | CAT.#: R357-48W-2 | Price: $1,700.00 | |
| Cultured RCm: Fresh, Plated Cells in Maintenance Medium | Size: 2 of 96-Well Multiwell | CAT.#: R357-96W-2 | Price: $1,766.00 | |
| Cultured RCm: Fresh, Plated Cells on inserts in Maintenance Medium | Size: 2 of 6-Well Multiwell, w/ Inserts | CAT.#: R357-6i-2 | Price: $1,442.00 | |
| Cultured RCm: Fresh, Plated Cells on inserts in Maintenance Medium | Size: 2 of 12-Well Multiwell, w/ Inserts | CAT.#: R357-12i-2 | Price: $1,550.00 | |
| Cultured RCm: Fresh, Plated Cells on inserts in Maintenance Medium | Size: 2 of 24-Well Multiwell, w/ Inserts | CAT.#: R357-24i-2 | Price: $1,658.00 |
Related Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCm Culture Medium: All-in-one ready-to-use media | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: R313-500 | Price: $131.00 | |
| RCm Culture Medium Kit: Basal medium & growth supplement sold together packaged separately | Size: Yields 500 ml | CAT.#: R313K-500 | Price: $145.00 | |
| RCm Basal Medium: Basal medium (contains no growth supplement). Add GS before use. | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: R312-500 | Price: $76.00 | |
| RCm Culture Supplement: Added to Basal Medium to create Culture Medium | Size: 80 ml | CAT.#: R313-GS | Price: $51.00 | |
| RCm Culture Medium wo FBS: Culture medium without FBS | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: R313F-500 | Price: $143.00 | |
| RCm Culture Medium w/ FBS or Horse Serum: Culture medium without FBS and horse serum | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: R313FH-500 | Price: $143.00 |
Extended Family Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freezing Medium: For general cryopreservation of most primary cells. Contains FBS & DMSO. | Size: 50 ml | CAT.#: 040-50 | Price: $54.00 |
Resources/Documents
Publications
2012
Das, B., R. Bayat-Mokhtari, M. Tsui, S. Lotfi, R. Tsuchida, D. Felsher, and H. Yeger. 2012. HIF-2α Suppresses p53 to Enhance the Stemness and Regenerative Potential of Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cells, 30:1685-1695.
Zhang, T., Z. Li, H. Dang, R. Chen, C. Liaw, T. Tran, P. Boatman, D. Connolly and J. Adams. 2012. Inhibition of Mas G-protein signaling improves coronary blood flow, reduces myocardial infarct size, and provides long-term cardioprotection. Am J Physiol, Heart & Circ Physiol, 302:H299-H311.
2011
Zhang, T., Z. Li, H. Dang, R. Chen, C. Liaw, T.-A. Tran, P.D. Boatman, D.T. Connolly, and J.W. Adams. 2011. Inhibition of Mas G-protein signaling improves coronary blood flow, reduces myocardial infarct size, and provides long-term cardioprotection. American Journal of Physiology - Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 302:H299-H311.
2010
French, K.J., R.W. Coatney, J.P. Renninger, C.X. Hu, T.L. Gales, S. Zhao, L.M. Storck, C.B. Davis, J. McSurdy-Freed, E. Chen, and K.S. Frazier. 2010. Differences in Effects on Myocardium and Mitochondria by Angiogenic Inhibitors Suggest Separate Mechanisms of Cardiotoxicity. Toxicologic pathology. 38:691-702.
2008
Sun, C., C. Fang, Z. Stephen, O. Veiseh, S. Hansen, D. Lee, R.G. Ellenbogen, J. Olson, and M. Zhang. 2008. Tumor-targeted drug delivery and MRI contrast enhancement by chlorotoxin-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 3:495-505.
2007
Jain, R., P.W. Shaul, Z. Borok, and B.C. Willis. 2007. Endothelin-1 induces alveolar epithelial–mesenchymal transition through endothelin type A receptor–mediated production of TGF-β1. American J. Resp. Cell & Mol.Biol. 37:38.
Yalamanchili, P., E. Wexler, M. Hayes, M. Yu, J. Bozek, M. Kagan, H.S. Radeke, M. Azure, A. Purohit, D.S. Casebier, and S.P. Robinson. 2007. Mechanism of uptake and retention of F-18 BMS-747158-02 in cardiomyocytes: A novel PET myocardial imaging agent. Journal of Nuclear Cardiology. 14:782-788.
2006
Hamm, E.E., D.E. Voth, and J.D. Ballard. 2006. Identification of Clostridium difficile toxin B cardiotoxicity using a zebrafish embryo model of intoxication. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 103:14176-14181.
Matesic, D.F., D.N. Abifadel, E.L. Garcia, and M.W. Jann. 2006. Effect of thioridazine on gap junction intercellular communication in connexin 43-expressing cells. Cell biology and toxicology. 22:257-268.
Zhang, M., S. Wang, N. Kohler, Y. Lin, and C. Sun. 2006. Methotrexate-modified nanoparticles and related methods. Patent US 20070269380 A1.
2005
Chen, Y., P.S. Gill, and W.J. Welch. 2005. Oxygen availability limits renal NADPH-dependent superoxide production. American Journal of Physiology - Renal Physiology. 289:F749-F753.
Willis, B.C., J.M. Liebler, K. Luby-Phelps, A.G. Nicholson, E.D. Crandall, R.M. du Bois, and Z. Borok. 2005. Induction of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Alveolar Epithelial Cells by Transforming Growth Factor-β1: Potential Role in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. The American journal of pathology. 166:1321-1332.
