Instructions HFLS Normal
MSDS Cryopreserved Cells
Cell Apps Flyer Skeletal System Cells
5 Important Cell Culture Rules
Cell Apps Poster Primary Cells
Cell Applications Inc Brochure
Description
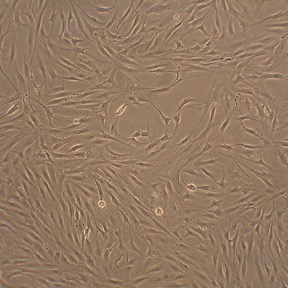
Human Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes (HFLS) provide an excellent cellular model for studying the normal and pathological physiology of synoviocytes and development of joint diseases.
Normal HFLS from Cell Applications, Inc. have been used to examine:
- TNFα – mediated changes in gene expression
- TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) contribution to joint inflammation by inducing chemokines and matrix metalloprotease-9, suggesting TWEAK as a new therapeutic target
- The role of miR-124a in arthritis pathogenesis
- C/EBPβ regulation of metalloproteinases and ADAMTS family members in synoviocytes stimulated with IL-1β
- HMW-HA suppression of ADAMTS4 mRNA and protein expression via CD44, p38 MAPK and JNK pathways
- Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic activity of various compounds, such as NF-κB inhibitors, AGIX-4207, HA–methotrexate conjugates and bucillamine
- Reactive arthritis triggered by chlamydial infection
- Mechanisms of arthritis-like syndrome in patients infected with chikungunya (CHIK) virus
- Use of Leukocyte-poor, RBC-free platelet-rich plasma in clinical orthopaedics, because leukocytes and RBCs cause synoviocyte death and proinflammatory mediator production
- Cartilage link protein and MAGP2 as markers to distinguish chondrocytes and synovial cells
- Creation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) by using the now classic “Yamanaka cocktail”, the discovery for which Dr. Shinya Yamanaka was awarded the Nobel Prize in 2012
- Causative agents, immunopathological mechanisms and signal transduction pathways leading to joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis
- The role of estrogen signaling in increasing inflammation
- Anti-inflammatory properties of herbal compound Sinomenine suggested for rheumatoid arthritis treatment
- Effects of extracellular matrix composition on cell attachment and migration relevant to T-cell function in inflamed tissues
- The role of human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) in development of rheumatoid arthritis
- Activated expression of different forms of HERV, contributing to development of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms by different mechanisms
Details
Tissue | Normal healthy human synovial tissue |
QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma, virus |
Bioassay | Attach, spread, proliferate in Growth Med |
Cryovial | 500,000 HFLS (2nd passage) frozen in Basal Medium w/ 10% FBS, 10% DMSO |
Kit | Cryovial frozen HFLS (408-05a), Growth Medium (415-500), Subcltr Rgnt Kit (090K) |
Proliferating | Shipped in Gr Med, 3rd psg (flasks or plates) |
Doublings | At least 5 |
Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Human Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Normal Tissue Total Kit, adult: 5x10^5 Cells (Adult), Medium & Subculture Reagents (See Details tab for specifics). | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: 408K-05a | Price: $1,179.00 | |
| Cryopreserved Synoviocytes (HFLS), adult: Frozen HFLS (5x10^5). | Size: 1 Cryovial | CAT.#: 408-05a | Price: $985.00 | |
| Proliferating Synoviocytes (HFLS), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium. Estimated release June 2021. | Size: T-25 Flask | CAT.#: 409-25a | Price: $985.00 | |
| Proliferating Synoviocytes (HFLS), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium. Estimated release June 2021. | Size: T-75 Flask | CAT.#: 409-75a | Price: $1,175.00 | |
| Proliferating Synoviocytes (HFLS), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium. Estimated release June 2021. | Size: 96 Well | CAT.#: 409-96Wa | Price: $1,295.00 |
Related Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFLS Growth Medium: All-in-one ready-to-use | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 415-500 | Price: $135.00 | |
| HFLS Growth Medium Kit: Basal medium & growth supplement sold together packaged separately | Size: Yields 500 ml | CAT.#: 415K-500 | Price: $146.00 | |
| HFLS Basal Medium: Basal medium (contains no growth supplement). Add GS before use. | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 414-500 | Price: $81.00 | |
| HFLS Growth Supplement: Added to Basal Medium to create Growth Medium | Size: 50 ml | CAT.#: 415-GS | Price: $85.00 | |
| HFLS Growth Medium wo Antibiotics: Growth medium without antibiotics | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 415A-500 | Price: $146.00 | |
| HFLS Growth Medium wo FBS: Growth medium without FBS | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 415F-500 | Price: $146.00 |
Extended Family Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synoviocytes RNA (HFLS RNA), Adult: Total RNA prepared from Human Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes, adult | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: 408-R10a | Price: $398.00 | |
| Synoviocytes RNA (HFLS RNA), Adult: Total RNA prepared from Human Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes, adult | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: 408-R25a | Price: $796.00 |
Resources/Documents
Citations
Publications
2017
Fan, W., W. Wang, J. Wu, L. Ma and J. Guo. 2017. Identification of CD4+ T-cell-derived CD161+ CD39+ and CD39+CD73+ microparticles as new biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. Future Medicine, 11:107-116.
Yuki, A., T. Mitsuyoshi, R. Kunimatsu, N. Hirose, S. Su, T. Awada, K. Tanne and K. Tanimoto. 2017. Hyaluronan enhances proteoglycan4 expression in synovial cells. Mes Res Arch, 51:1-56.
2016
Jones, D., A. Jenny, J. Swantek, J. Burke, D. Lauffenburger and P. Sorger. 2016. Profiling drugs for rheumatoid arthritis that inhibit synovial fibroblast activation. Nature Chemical Biology, doi:10.1038/nchembio.2211.
Jin, L., Y. Nonaka, S. Miyakawa, M. Fujiwara and Y. Nakamura. 2016. Dual Therapeutic Action of a Neutralizing Anti-FGF2 Aptamer in Bone Disease and Bone Cancer Pain. Mole Ther, 24:1974-1986.
Lin, Z., C. Lee, M. Tsai, H. Ko, J. Fang, Y. Chiang, C. Liang, L. Hsu, S. hu and F. Yen. 2016. Eupafolin nanoparticles protect HaCaT keratinocytes from particulate matter-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. Intl J Nanomedicine, 11:3907, 3926.
Zimmermann-Geller, B., S. Köppert, S. Fischer, H. Cabrera-Fuentes, S. Lefèvre, M. Rickert, J. Steinmeyer, S. Rehart, T. Umscheid, M. Schönburg, U. Müller-Ladner, K. Preissner, K. Frommer and E. Neumann. 2016. Influence of Extracellular RNAs, Released by Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts, on Their Adhesive and Invasive Properties. J Immunol, 197:2589-2597.
2015
Calabro, A., M. Lauer, and V. Hascall. 2015. Treatment of extracellular matrix to reduce inflammation. Patent US 9012395 B2.
Jie, L., R. Huang, W. Sun, S. Wei, Y. Chu, Q. Huang, and H. Du. 2015. Role of cysteine‑rich angiogenic inducer 61 in fibroblast‑like synovial cell proliferation and invasion in rheumatoid arthritis. Molecular Medicine Reports, 11:917-923.
McCoy, J., D. Walkenhorst, K. McCauley, H. Elaasar, J. Everett, and K. Mix. 2015. Orphan nuclear receptor NR4A2 induces transcription of the immunomodulatory peptide hormone prolactin. Journal of Inflammation, 12:13. DOI 10.1186/s12950-015-0059-2.
Padley, R. and R. Heuser. 2015. Compositions and Methods for Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis. Patent Application US20150291689A1.
Wardell, P, M. Forstner and A. Bader. 2015. Investigation of the cytokine response to NF-κB decoy oligonucleotide coated polysaccharide based nanoparticles in rheumatoid arthritis in vitro models. Arthritis Res & Ther, 17:310.
2014
Braun, H.J., H.J. Kim, C.R. Chu, and J.L. Dragoo. 2014. The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma Formulations and Blood Products on Human Synoviocytes: Implications for Intra-articular Injury and Therapy. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 10.1177/0363546514525593.
Brys, R., N. Vandeghinste, P. Tomme, and H. Klaassen. 2014. Molecular targets and compounds, and methods to identify the same, useful in the treatment of joint degenerative and inflammatory diseases. Patent US 8673268 B2.
Calabro, A., M. Lauer, and V. Hascall. 2014. Treatment of extracellular matrix to reduce inflammation. Patent Application US 20140135256 A1.
Calabro, A., M. Lauer, and V. Hascall. 2014. Treatment of extracellular matrix to reduce inflammation. Patent US 8658593 B2.
2013
Kataoka, Y., W. Ariyoshi, T. Okinaga, T. Kaneuji, S. Mitsugi, T. Takahashi, and T. Nishihara. 2013. Mechanisms involved in suppression of ADAMTS4 expression in synoviocytes by high molecular weight hyaluronic acid. In Biochemical and biophysical research communications: 432. 580-585.
Matsumoto, Y., H. Ichihara, M. Hino, M. Umebayashi, and R. Ueoka. 2013. Therapeutic effects of hybrid liposomes without drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Delivery: doi:10.3109/10717544.10712013.10869635.
Phuklia, W., J. Kasisith, N. Modhiran, E. Rodpai, M. Thannagith, T. Thongsakulprasert, D.R. Smith, and S. Ubol. 2013. Osteoclastogenesis induced by CHIKV-infected fibroblast-like synoviocytes: A possible interplay between synoviocytes and monocytes/macrophages in CHIKV-induced arthralgia/arthritis. Virus research. 177:179-188.
2012
Evanko, S.P., S. Potter-Perigo, P.L. Bollyky, G.T. Nepom, and T.N. Wight. 2012. Hyaluronan and versican in the control of human T-lymphocyte adhesion and migration. Matrix Biology. 31:90-100.
Hsu, J., Y. Gu, S.-L. Tan, S. Narula, J.A. DeMartino, and C. Liao. 2012. Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase mediates platelet receptor-induced generation of microparticles: A potential mechanism for amplification of inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis synovial joints. Immunology letters, 150:97-104.
Rapko, S., and S. Duguay. 2012. Methods of evaluating cells and cell cultures. Patent Application US 20120329051 A1.
Tsuji, F., K. Oh-hashi, and K. Kiuchi. 2012. Differential effects of Akt pathway inhibitors on IL-1β-induced protein phosphorylation in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Journal of Receptors and Signal Transduction. 32:22-28.
Tsushima, H., K. Okazaki, M. Hayashida, T. Ushijima, and Y. Iwamoto. 2012. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β regulates expression of matrix metalloproteinase-3 in arthritis. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 71:99-107.
2011
Chen, D.P., C.K. Wong, L.S. Tam, E.K. Li, and C.W. Lam. 2011. Activation of human fibroblast-like synoviocytes by uric acid crystals in rheumatoid arthritis. Cellular & molecular immunology. 8:469-478.
Rapko, S., and S. Duguay. 2011. Methods of evaluating cells and cell cultures. Patent Application US 20120149013 A1.
Yamanaka, S., and K. Takahashi. 2011. Oct3/4, Klf4, c-Myc and Sox2 produce induced pluripotent stem cells. Patent US 8058065 B2.
2010
El-Beialy, W., N. Galal, Y. Deyama, Y. Yoshimura, K. Suzuki, K. Tei, and Y. Totsuka. 2010. Effects of Estrogen on PMCA 2 and 4 in Human Fibroblast-like Synovial Cells and Mouse Macrophage-like Cells. Endocrine J, 57:93-97.
Freimanis, G., P. Hooley, H.D. Ejtehadi, H. Ali, A. Veitch, P. Rylance, A. Alawi, J. Axford, A. Nevill, and P.G. Murray. 2010. A role for human endogenous retrovirus‐K (HML‐2) in rheumatoid arthritis: investigating mechanisms of pathogenesis. Clinical & Experimental Immunology. 160:340-347.
Rapko, S., M. Zhang, B. Richards, E. Hutto, S. Dethlefsen, and S. Duguay. 2010. Identification of the Chondrocyte Lineage Using Microfibril-Associated Glycoprotein-2, A Novel Marker That Distinguishes Chondrocytes from Synovial Cells. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 16:1367-1375.
2009
Itoh, Y., N. Hatano, H. Hayashi, K. Onozaki, K. Miyazawa, and K. Muraki. 2009. An environmental sensor, TRPV4 is a novel regulator of intracellular Ca2+ in human synoviocytes. American Journal of Physiology. 297:C1082-C1090.
Nakamachi, Y., S. Kawano, M. Takenokuchi, K. Nishimura, Y. Sakai, T. Chin, R. Saura, M. Kurosaka, and S. Kumagai. 2009. MicroRNA‐124a is a key regulator of proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 secretion in fibroblast‐like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 60:1294-1304.
Oki, K., F. Tsuji, K. Ohashi, M. Kageyama, H. Aono, and M. Sasano. 2009. The investigation of synovial genomic targets of bucillamine with microarray technique. Inflammation Research. 58:571-584.
2008
Galal, N., W.E. Beialy, Y. Deyama, Y. Yoshimura, T. Yoshikawa, K. Suzuki, and Y. Totsuka. 2008. Effect of estrogen on bone resorption and inflammation in the temporomandibular joint cellular elements. Int. J. Mol. medicine. 21:785.
Mathieu, M.C., S. Lord‐Dufour, V. Bernier, Y. Boie, J.D. Burch, P. Clark, D. Denis, Y. Han, J.R. Mortimer, and A.G. Therien. 2008. Mutual antagonistic relationship between prostaglandin E2 and IFN‐γ: Implications for rheumatoid arthritis. European journal of immunology. 38:1900-1912.
Pappas, J., and P. Yang. 2008. Human ESC vs. iPSC—Pros and Cons. J Cardiovascular Translational Res, 1:96-99.
Yamanaka, S., K. Takahashi, and M. Nakagawa. 2008. Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells. Patent Application US 20090047263 A1.
2007
Carman, J., S. Nadler, M. Bowen, M. Neubauer, and P. Lu. 2007. Antiinflammatory agents; antiarthritic agents; determination gene expression of cell binding to drugs; calibration. Patent US 7244573 B2
Harigai, T., H. Hagiwara, Y. Ogawa, T. Ishizuka, S. Kaneda, and J. Kimura. 2007. Prednisolone phosphate‐containing TRX‐20 liposomes inhibit cytokine and chemokine production in human fibroblast‐like synovial cells: a novel approach to rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Journal of pharmacy and pharmacology. 59:137-143.
Ikeda-Dantsuji, Y., I. Konomi, and A. Nagayama. 2007. Effects of levofloxacin and doxycycline on interleukin-6 production of Chlamydia trachomatis-infected human synovial fibroblasts. Chemotherapy. 53:332-337.
Rapko, S., U. Baron, U. Hoffmüller, F. Model, L. Wolfe, and S. Olek. 2007. DNA methylation analysis as novel tool for quality control in regenerative medicine. Tissue engineering. 13:2271-2280.
Takahashi, K., K. Tanabe, M. Ohnuki, M. Narita, T. Ichisaka, K. Tomoda, and S. Yamanaka. 2007. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 131:861-872.
Tsuji, F., I. Seki, H. Aono, N. Odani, K. Mizutani, M. Okamoto, and M. Sasano. 2007. Bucillamine mechanism inhibiting IL-1β-induced VEGF production from fibroblast-like synoviocytes. International Immunopharmacol. 7:1569-1576.
2006
Wen, D., Y. Nong, J.G. Morgan, P. Gangurde, A. Bielecki, J. DaSilva, M. Keaveney, H. Cheng, C. Fraser, and L. Schopf. 2006. A selective small molecule IκB kinase β inhibitor blocks nuclear factor κB-mediated inflammatory responses in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes, chondrocytes, and mast cells. J. Pharmacol. & Experimental Therapeutics. 317:989-1001.
2005
Kunsch, C., J. Luchoomun, X.-l. Chen, G.L. Dodd, K.S. Karu, C.Q. Meng, E.M. Marino, L.K. Olliff, J.D. Piper, and F.-H. Qiu. 2005. AGIX-4207 [2-[4-[[1-[[3, 5-Bis (1, 1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl] thio]-1-methylethyl] thio]-2, 6-bis (1, 1-dimethylethyl) phenoxy] acetic acid], a novel antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound: cellular and biochemical characterization of antioxidant activity and inhibition of redox-sensitive inflammatory gene expression. J.Pharmacol.& Exp. Therap. 313:492-501.
Ota, T., T. Isogai, T. Nishikawa, K. Hayashi, K. Otsuka, J. Yamamoto, S. Ishii, T. Sugiyama, A. Wakamatsu, K. Nagai, T. Otsuki, S. Funahashi, S. Miyata, K. Sobue, and K. Hayashi. 2005. The protein encoded by novel gene has two WW domains that participate in protein interactions in the N-terminal domain, and this protein binds to other proteins, thus regulates the intracellular signal transduction, gene expression. Patent US 6908748 B2.
Wada, Y., K. Shimada, T. Kimura, and S. Ushiyama. 2005. Novel p38 MAP kinase inhibitor R-130823 suppresses IL-6, IL-8 and MMP-13 production in spheroid culture of human synovial sarcoma cell line SW 982. Imm. lett. 101:50-59.
2004
Patturajan, M., I. Millet, S. Kumar, C. Miller, P. Mezes, D. Lepley, C. Burgess, and R. Shimkets. 2004. Novel fibroblast growth factor and uses thereof. Patent Application US 20060141565 A1.
Tanaka, K., H. Moriaoka, T Morii, H. Matsumoto, L. Weisshbacc,, and F. Hornicek. 2004. DOWN REGULATION OF VEGF EXPRESSION IN HUMAN FIBROBLAST LIKE SYNOVIOCYTES BY NOVEL ANTI ANGIOGENIC PROTEIN PLASMINOGEN RELATED PROTEIN. 51st Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society, Poster No: 1490.
2002
Sugiyama, T., S. Ishii, J.-i. Yamamoto, R. Irie, K. Saito, T. Otuki, A. Wakamatsu, Y. Suzuki, Y. Hio, T. Ota, T. Nishikawa, S. Sugano, Y. Masuho, and T. Isogai. 2002. cDNA macroarray analysis of gene expression in synoviocytes stimulated with TNFα. FEBS letters. 517:121-128.
1999
Tsuji, F., K. Oki, T. Senda, M. Horiuchi, and S. Mita. 1999. Effects of mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors or phosphodiesterase inhibitors on interleukin-1-induced cytokines production in synovium-derived cells. Immunology letters. 68:275-279.