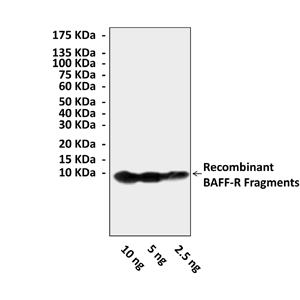
Description
BACKGROUND BAFF (B cell activating factor), a member of the TNF family (also termed TALL-1, THANK, BlyS and zTNF4) and BAFF receptor (BAFF-R) play a fundamental role during the transition from immature T1 to T2 B cells and therefore for the generation of mature B cells in the spleen. This was clearly demonstrated by an almost complete lack of follicular and marginal zone B cells and by a block at the T1 cell stage in BAFF as well as in BAFF-R deficient mice. In these mice, the B-1 compartment was not affected, indicating that the development of this subset was independent of BAFF-BAFF-R signaling. On the other hand, transgenic mice over-expressing BAFF display an overall increase in all B cell subsets, suggesting that all mature B cells express BAFF-R on their surface or are able to respond to BAFF.1
BAFF-R (also called BR3) is the most unique of the 3 tumor necrosis factor receptors (TNFRs) for BLyS (B-lymphocyte stimulator; also called BAFF). A/WySNJ mice (which have a mutant BAFF-R gene) have a low peripheral blood B-cell fraction that is similar to that seen in BLyS-deficient mice, suggesting that BAFF-R transmits critical B-cell survival signals associated with BLyS stimulation. Downstream mediators of BAFF-R activation include both the canonical (classic, NF-κB1) and alternative (noncanonical, NF-κB2) NF-κB pathways. Although BLyS/BAFF-R–derived intracellular signaling pathways are still incompletely defined, this ligand/receptor dyad provides key regulatory control of antiapoptotic cell survival and growth stimulation. In this regard, BLyS modulates several antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members, including Bcl-xL, Mcl-1, A-1, Bcl-2, and Bim, via survival-promoting kinase systems such as Pim 1/2 or Erk as well as proteins involved in early cell-cycle progression, including c-myc, p27Kip1, cyclin D1, and cyclin D2. The binding of BAFF to the BAFF-R leads to the activation of the NF-κB pathway and ultimately to the transcription of the anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2. The finding that Bcl-2 over-expression can, to a large extent, rescue the mature B cell compartment in BAFF signaling deficient mice, indicates that Bcl-2 expression induced by BAFF is crucial for the survival of B cells during the transition from immature to mature stages. Moreover, BAFF-BAFF-R signaling was also playing a central role in the in vivo maintenance of the peripheral mature B cell pool.2 Furthermore, BAFF-R was found to be presented in the cell nucleus as well as in the plasma membrane and cytoplasm, in both normal peripheral blood B lymphocytes and aggressive NHL-B cells. It demonstrated that in addition to activating the NF-κB pathways in the plasma membrane, BAFF-R can also promote normal and NHL-B-cell survival and proliferation by directly functioning as a transcriptional cofactor with other NF-κB transcription factor(s) and possibly regulating transcription of other NF-κB target genes.3
3. Fu, L. et al:Blood 113:4627-36, 2009
Details
Cat.No.: | CA1391 |
Antigen: | A short peptide from human BAFF-R sequence. |
Isotype: | Rabbit IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:500 - 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 - 1:100 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 25 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous BAFF-R proteins without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbit B Cell Activating Factor Receptor Anitbody: Rabbit B Cell Activating Factor Receptor Anitbody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CA1391 | Price: $302.00 |