Product Sheet CP10086
Description
BACKGROUND Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases consists of at least 14 distinct receptors and has eight membrane-bound ligands, known as the ephrins. This is the largest family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Eph proteins are divided into two subfamilies: the EphA receptors (A1-A8) that bind glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked ephrin-A ligands (A1-A5), and the EphB receptors (B1-B6) that bind transmembrane ephrin-B ligands (B1-B3). The only known crosstalk between the A and B subfamilies occurs with the EphA4 receptor, which can bind ephrins-B2 and -B3 as well as the entire A subclass. There is a great deal of redundancy of receptor-ligand binding specificity within each subfamily, although binding affinities vary.1,2 Both GPI-anchoredephrinA and transmembrane ephrinB ligands interact with the Nterminal globular domain (Glob) of Eph receptors. The Eph receptors become phosphorylated at specific tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domain following ligand binding. Phosphorylated motifs serve as sites of interaction with certain cytoplasmic signaling proteins to mediate downstream signaling. In addition, through their C terminus the Eph receptors associate with PDZ (postsynaptic density protein, disc large, zona occludens) domain-containing proteins. Moreover, Eph receptor contact induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of ephrinB proteins via an SRC-family kinase (SFK), which mediating the reverse signaling. One of the unique features of Eph/ephrin signaling is the fact that both receptors and ligands are competent to transduce a signaling cascade upon interaction. Eph-activated signaling is termed forward, and ephrin-activated signaling is termed reverse. Another level of complexity stems from the fact that interactions between Eph receptors and ephrins can happen in trans (between two opposing cells) or in cis (within the same cell). It is commonly assumed that trans interactions are activating while cis interactions are inhibiting.3 Eph-Ephrin signaling functions in a variety biological processes including diverse assegmentation of the somites and rhombomeres, the formation of blood vessels, Axon guidance and fasciculation, migration of the neural crest and metastasis of transformed cells etc.
EphB4 was originally isolated from the mature mouse mammary gland, and tightly controlled expression was observed during mammary gland development and experimental carcinogenesis. EphB4 and its ligand ephrin-B2 are intimately involved in the development of the vascular system during embryogenesis. EphB4, are expressed in adult organs such as the kidney, lung and mammary gland. Expression of the ephrin-B2 ligand was confined to the epithelial cells, whereas the EphB4 receptor was expressed in both the myoepithelial and epithelial cells. Interestingly, the epithelial expression of EphB4 was only observed during proliferative phases of mammary gland development, such as puberty and the follicular phase of the cycle. It was demonstrate that unscheduled expression of EphB4 interferes with the architecture of the mammary epithelial tree, alters the response of the epithelial cells to proliferative and apoptotic signals and contributes to the invasive phenotype of mouse mammary tumours.4 EphB4 receptor suppresses breast cancer cell tumorigenicity through an Abl–Crk pathway.5
REFERENCES
1. Brantley-Sieders, D.M. & Chen, J. : Angiogenesis. 7:17, 2004
2. Murai, K.K. & Pasquale, E.B. : J. Cell Sci. 116:2823, 2003
3. Arvanitis, D. & Davy, A.: Genes & Dev. 22:416, 2008
4. Munarini, N. et al: J. Cell Sci.115:25-37, 2002
5. Noren, N.K. et al: Nature Cell Biol. 8:815-25, 2006
2. Murai, K.K. & Pasquale, E.B. : J. Cell Sci. 116:2823, 2003
3. Arvanitis, D. & Davy, A.: Genes & Dev. 22:416, 2008
4. Munarini, N. et al: J. Cell Sci.115:25-37, 2002
5. Noren, N.K. et al: Nature Cell Biol. 8:815-25, 2006
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
Cat.No.: | CP10086 |
Antigen: | Purified recombinant human EphB4 fragments expressed in E. coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC n/d ICC n/d FACS n/d |
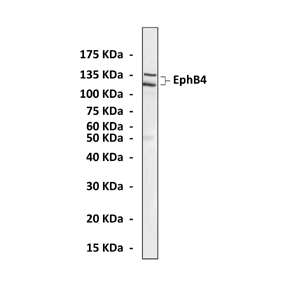
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 128/135 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous EphB4 proteins in cells without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse EphB4 Antibody: Mouse EphB4 Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CP10086 | Price: $354.00 |