Product Sheet CP10378
Description
BACKGROUND The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a member of the steroid/thyroid/retinoic acid receptor superfamily. It has demonstrated that multiple isoforms of human GR are generated from one single gene and one mRNA species by the mechanisms of alternative RNA splicing and alternative translation initiation. These isoforms display diverse cytoplasm-to-nucleus trafficking patterns and distinct transcription activities. In addition, each hGR protein can be subjected to a variety of post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, sumoylation and ubiquitination. The hGR consists of a centrally located DNA-binding domain, a steroid-binding domain located in the carboxy terminal and an immunogenic domain in the amino terminal half.1 Binding of glucocorticoids to the GCR is noncovalent, and triggers a process through which the GR converts from its non-DNA-binding to its DNA-binding form. Upon activation the glucocorticoid-GR-complex translocates to the nucleus, traversing the nuclear membrane probably by a facilitated transport mechanism. The hGR regulates the rate of transcription initiation from promoter-sites by binding to specific sequences in the genome, known as hormone-responsive elements (HRE) or glucocorticoid-responsive elements (GRE). Through regulation of various target gene expressions, RA participates in wide ranges of essential biological processes including growth, development, metabolism, behavior and apoptosis.2 There is compelling evidence that phosphorylation regulates the activity of the steroid receptor superfamily. The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is phosphorylated at multiple sites within its N terminus (S203, S211, S226). It was demonstrated that cyclin E/cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (Cdk2) phosphorylates GR at S203, whereas cyclin A/Cdk2 phosphorylates both S203 and S211. In addition, GR S211 also appears to be a substrate for p38 MAPK. And S226 is phosphorylated by JNK.3 GR phosphorylation at S211 and S226 determines GR transcriptional response by modifying cofactor interaction.
REFERENCES
1. Gustafsson, JA et al: Endocrine Rev 8:185-234, 1987.
2. Zhou, J & Cidlowski JA:Steroids 70:407-417, 2005.
3. Chen, W. et al: Mol Endocrinol. 22: 1754–1766, 2008.
2. Zhou, J & Cidlowski JA:Steroids 70:407-417, 2005.
3. Chen, W. et al: Mol Endocrinol. 22: 1754–1766, 2008.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
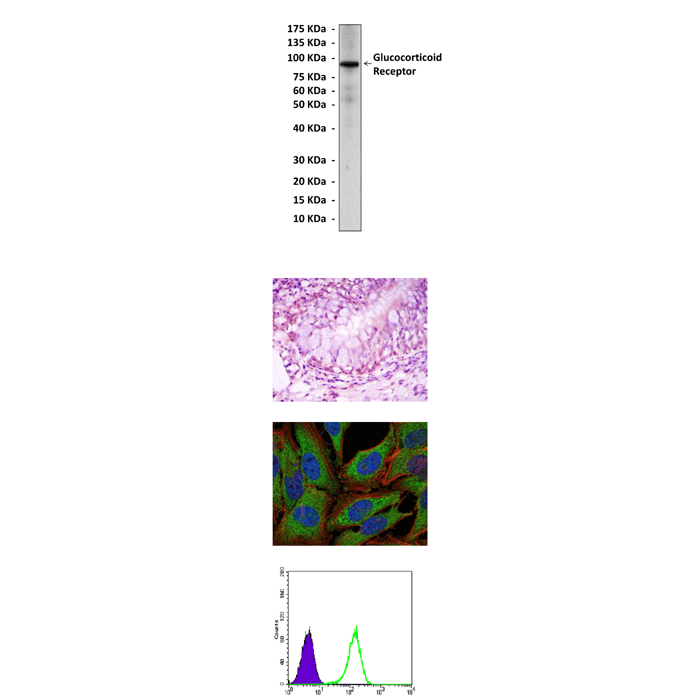
(Click to Enlarge) Top: Western Blot detection of glucocorticoid receptor proteins in HeLa cell lysate using glucocorticoid receptor antibody. Middle Upper: This antibody stains paraffin-embedded human lung cancer tissue in immunohistochemical analysis. Middle Lower: It also stains PC-2 cells in confocal immunofluorescent assay (Glucocorticoid receptor antibody: Green; Actin filaments: Red; DRAQ5 DNA Dye: Blue). Bottom: This antibody specifically reacts with glucocorticoid receptor proteins in K562 cells as shown by FACS (Glucocorticoid receptor antibody: Green; control mouse IgG: purple).
Details
Cat.No.: | CP10378 |
Antigen: | Raised against purified recombinant fragments of human glucocorticoid receptor expressed in E. Coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 - 1:200 ICC 1:50 - 1:200 FACS 1:50 - 1:200 |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 95 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects glucocorticoid receptor proteins without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse Glucocorticoid Receptor Antibody: Mouse Glucocorticoid Receptor Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CP10378 | Price: $457.00 |
