Product Sheet CL0310
Description
BACKGROUND The BMPs (bone morphogenetic proteins) are a group of related proteins originally identified by their presence in bone-inductive extracts of demineralized bone. These molecules are part of the TGF-beta superfamily, based on primary amino acid sequence homology, including the absolute conservation of seven cysteine residues between the TGF-betas and the BMPs. BMPs have been divided into subgroups based on structural and evolutionary considerations. Although closely related BMPs have been shown to elicit distinct cellular responses, members within a subgroup often display conservation of not only structure, but also function.1 BMPs signal through type I and II serine/threonine kinase receptors that phosphorylate the downstream target proteins Smads. Activation of type I BMP receptor phosphorylates Smad1, Smad5, and presumably Smad8 and associates with Smad4 in a heteromeric complex that is translocated to the nucleus, where it activates transcription. TGF-beta binding to receptors leads to phosphorylated Smad2 and Smad3, which associate with Smad4, and the complex can translocate to the nucleus to regulate transcriptional activity. The Smad signaling pathway has been shown to play a role in BMP-2-induced osteoblast differentiation. However, other signaling pathways, such as extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2), protein kinase C, and cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) may also be involved in the BMP-induced effects on bone cells. It was shown that PI-3 kinase/Akt pathway was involved in BMP-2 induced osteoblast differentiation.2 Another cascade is activated by TGF-beta and BMP-4 and involves TGF-beta-activated kinase-1 (TAK1), a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase family, p38, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase.2
BMP-5, one of the more prominently expressed BMPs in the nervous system, has been detected in multiple regions of the nervous system throughout development and into adulthood. BMP-5 belongs to the 60A subgroup of BMPs, which also includes BMP-6/Vgr-1, BMP-7/OP-1, BMP-8a/OP-2, BMP-8b and Drosophila 60A. Other members of the 60A subgroup have been shown to modulate neuronal morphogenesis through selective effects on dendrites. Thus, BMPs 6, 7, and 60A stimulate dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons derived from either perinatal or adult ganglia in the absence of effects on cell survival or axonal growth. BMP-7 has also been shown to enhance dendritic growth in hippocampal, cortical and spinal motor neurons. A role for BMP-5 in dorsal forebrain patterning has been proposed based on its expression in the dorsal midline of the developing forebrain and observations that ectopic expression of BMP-5 in the developing neural tube of chicks markedly downregulates ventral markers while maintaining dorsal markers.3 In addition, through phenotypes of short-ear (se) mice, which have BMP-5 mutations, a role for BMP-5 in some specific aspects of skeletogenesis and cartilage growth is known. It was demonstrated that BMP-5 is normally an important regulator of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation.4 Moreover, BMP-5 has been shown to be essential for nephrogenesis.
BMP-5, one of the more prominently expressed BMPs in the nervous system, has been detected in multiple regions of the nervous system throughout development and into adulthood. BMP-5 belongs to the 60A subgroup of BMPs, which also includes BMP-6/Vgr-1, BMP-7/OP-1, BMP-8a/OP-2, BMP-8b and Drosophila 60A. Other members of the 60A subgroup have been shown to modulate neuronal morphogenesis through selective effects on dendrites. Thus, BMPs 6, 7, and 60A stimulate dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons derived from either perinatal or adult ganglia in the absence of effects on cell survival or axonal growth. BMP-7 has also been shown to enhance dendritic growth in hippocampal, cortical and spinal motor neurons. A role for BMP-5 in dorsal forebrain patterning has been proposed based on its expression in the dorsal midline of the developing forebrain and observations that ectopic expression of BMP-5 in the developing neural tube of chicks markedly downregulates ventral markers while maintaining dorsal markers.3 In addition, through phenotypes of short-ear (se) mice, which have BMP-5 mutations, a role for BMP-5 in some specific aspects of skeletogenesis and cartilage growth is known. It was demonstrated that BMP-5 is normally an important regulator of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation.4 Moreover, BMP-5 has been shown to be essential for nephrogenesis.
REFERENCES
1. Wozney, J.M.: Prog. Growth Factor Res. 1:267-80, 1989
2. Chen, D. et al: Growth factors 22:233-41, 2004
3. Beck, H. N. et al: BMC Neurosci. 2:12, 2001
4. Mikic, B. et al: Bone 16:445-54, 1995
2. Chen, D. et al: Growth factors 22:233-41, 2004
3. Beck, H. N. et al: BMC Neurosci. 2:12, 2001
4. Mikic, B. et al: Bone 16:445-54, 1995
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
Cat.No.: | CL0310 |
Target Protein Species: | Human |
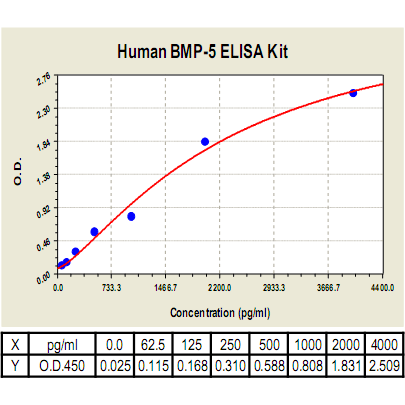
Range: | 62.5pg/ml-4000pg/ml |
Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokine. |
Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |
ELISA Kits are based on standard sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology. Freshly prepared standards, samples, and solutions are recommended for best results.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human BMP-5 ELISA Kit: Human Bone Morphogenic Protein-5 ELISA Kit | Size: 96 Wells | CAT.#: CL0310 | Price: $500.00 |