Product Sheet CL0445
Description
BACKGROUND Hemopoietic CSFs are glycoproteins that were initially characterized by their ability to stimulate in vitro the clonal proliferation of hemopoietic multipotential stem cells and/or mono- or bipotential progenitors in semisolid (agar or methylcellulose) medium. Furthermore, CSFs, which include interleukin-3 (IL-3, also named multi-CSF), granulocytemacrophage-CSF (GM-CSF), granulocyte-CSF (G-CSF), and colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1; also named macrophage-CSF, M-CSF) will induce the activity of mature, specialized myeloid cells and are required for their survival.1
CSF-1 is the lineage-specific growth factor stimulating the survival, proliferation and differentiation of the mononuclear phagocyte system (MNPS), from the determined but undifferentiated monoblast through to the mature macrophage. It is the primary regulator of production of these cells, including osteoclasts and also regulates cells of the female reproductive tract. CSF-1 is synthesized by a variety of different cell types, including fibroblasts, endothelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, osteoblasts, keratinocytes, astrocytes, myoblasts, under the control of the female steroid hormones during pregnancy, by uterine epithelial cells. It is homodimeric and secreted as an 80-100 kDa glycoprotein or a 130-160 kDa chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan or is expressed on the cell surface as a biologically active, membrane-spanning glycoprotein of 68-86 kDa. Studies that involve CSF-1-deficient mice demonstrate that there is a variable requirement for CSF-1 in the development of individual mononuclear phagocyte populations. However, these cells uniformly express the CSF-1 receptor, and their morphology, phagocytosis and responsiveness to infectious and non-infectious stimuli is regulated by CSF-1.2 CSF-1 plays important roles in innate immunity, cancer and inflammatory diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, arthritis, atherosclerosis and obesity. In several conditions, activation of macrophages involves a CSF-1 autocrine loop. In addition, secreted and cell-surface isoforms of CSF-1 can have differential effects in inflammation and immunity. CSF-1 binds to a single class of high-affinity cell surface receptors that are encoded by the proto-oncogene c- fms and belong to the receptor tyrosine kinase family. Expression of c- fms is considered a marker for the cells of the MNPS. It was also expressed on osteoclasts as well as embryonic cells, decidual cells and trophoblast.3
CSF-1 is the lineage-specific growth factor stimulating the survival, proliferation and differentiation of the mononuclear phagocyte system (MNPS), from the determined but undifferentiated monoblast through to the mature macrophage. It is the primary regulator of production of these cells, including osteoclasts and also regulates cells of the female reproductive tract. CSF-1 is synthesized by a variety of different cell types, including fibroblasts, endothelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, osteoblasts, keratinocytes, astrocytes, myoblasts, under the control of the female steroid hormones during pregnancy, by uterine epithelial cells. It is homodimeric and secreted as an 80-100 kDa glycoprotein or a 130-160 kDa chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan or is expressed on the cell surface as a biologically active, membrane-spanning glycoprotein of 68-86 kDa. Studies that involve CSF-1-deficient mice demonstrate that there is a variable requirement for CSF-1 in the development of individual mononuclear phagocyte populations. However, these cells uniformly express the CSF-1 receptor, and their morphology, phagocytosis and responsiveness to infectious and non-infectious stimuli is regulated by CSF-1.2 CSF-1 plays important roles in innate immunity, cancer and inflammatory diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, arthritis, atherosclerosis and obesity. In several conditions, activation of macrophages involves a CSF-1 autocrine loop. In addition, secreted and cell-surface isoforms of CSF-1 can have differential effects in inflammation and immunity. CSF-1 binds to a single class of high-affinity cell surface receptors that are encoded by the proto-oncogene c- fms and belong to the receptor tyrosine kinase family. Expression of c- fms is considered a marker for the cells of the MNPS. It was also expressed on osteoclasts as well as embryonic cells, decidual cells and trophoblast.3
REFERENCES
1. Nicola, N.A. & Metcalf, D.: Ciba Found Symp. 118:7-28, 1986
2. S K Das, S.K. & Stanley, E.R.: J. Biol. Chem. 257:13679-84, 1982
3. Pixley, F.J. & Stanley, E.R.:Trends Cell Biol. 14:628-38, 2004
2. S K Das, S.K. & Stanley, E.R.: J. Biol. Chem. 257:13679-84, 1982
3. Pixley, F.J. & Stanley, E.R.:Trends Cell Biol. 14:628-38, 2004
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
Cat.No.: | CL0445 |
Target Protein Species: | Mouse |
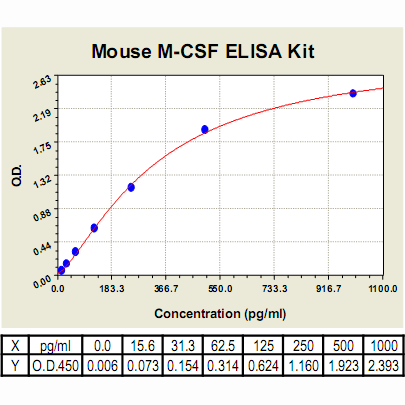
Range: | 15.6 pg/ml – 1000pg/ml |
Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokines |
Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |
ELISA Kits are based on standard sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology. Freshly prepared standards, samples, and solutions are recommended for best results.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse M-CSF ELISA Kit: Mouse Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor ELISA Kit | Size: 96 Wells | CAT.#: CL0445 | Price: $511.00 |