MSDS Cryopreserved Cells
Instructions HOb Normal
Cell Apps Flyer Skeletal System Cells
5 Important Cell Culture Rules
Cell Apps Poster Primary Cells
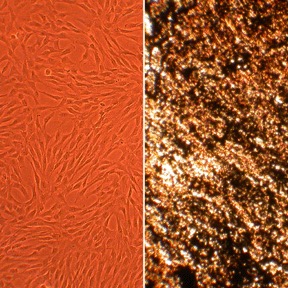
Description
Human Osteoblasts (HOb) from Cell Applications, Inc. are Isolated from fetal or adult human bones. The cells, positive for bone mineralization, provide an excellent model system for studies relevant to the skeletal system. Additionally, osteoblasts from osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis donors are available.
Our HOb have been used to examine:
- Actions, signaling pathways and cross-talk of growth factors, cytokines and interleukins
- Nuclear factors and gene expression
- Cell proliferation and differentiation
- Bone formation, morphogenesis, and bone morphogenic proteins
- Mechanisms behind bone disorders and defects including bone loss, osteoporosis, osteoclast inhibition, periodontitis, arthritis and related matrix metalloproteinase production
- Cancers, such as osteosarcoma and oncogenes. For the pharmaceutical industry, the cells have been pivotal in developing
- New pharmaceutical treatment strategies and drug delivery methods
- Orthopedic implants and tissue engineering have also been positively impacted by osteoblast research
Details
Tissue | Normal healthy human bone |
QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma, virus |
Character | Bone mineralization (Kossa stain) |
Bioassay | Attach, spread, proliferate in Growth Med |
Cryovial | 500,000 HOb (2nd passage) frozen in Basal Medium w/ 10% FBS, 10% DMSO |
Kit | Cryovial frozen HOb (406-05), Growth Medium (417-500), Subcltr Rgnt Kit (090K) |
Proliferating | Shipped in Gr Med, 3rd psg (flasks or plates) |
Doublings | At least 10 |
Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Human Osteoblasts Normal Tissue Total Kit, adult: 5x10^5 Cells (Adult), Medium & Subculture Reagents (See Details tab for specifics) | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: 406K-05a | Price: $1,047.00 | |
| Cryopreserved Osteoblasts (HOb), adult: Frozen HOb (5x10^5) | Size: 1 Cryovial | CAT.#: 406-05a | Price: $845.00 | |
| Cryopreserved Human Osteoblasts Normal Tissue Total Kit, fetal: 5x10^5 Cells, Medium & Subculture Reagents (See Details tab for Specifics) | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: 406K-05f | Price: $1,047.00 | |
| Cryopreserved Osteoblasts (HOb), fetal: Frozen HOb (5x10^5) | Size: 1 Cryovial | CAT.#: 406-05f | Price: $845.00 | |
| Proliferating Osteoblasts (HOb), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells, in medium | Size: T-25 Flask | CAT.#: 407-25a | Price: $845.00 | |
| Proliferating Osteoblasts (HOb), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells, in medium | Size: T-75 Flask | CAT.#: 407-75a | Price: $1,035.00 | |
| Proliferating Osteoblasts (HOb), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells, in medium | Size: 24 Well | CAT.#: 407-24Wa | Price: $1,035.00 | |
| Proliferating Osteoblasts (HOb), adult: Actively growing, dividing cells, in medium | Size: 96 Well | CAT.#: 407-96Wa | Price: $1,155.00 | |
| Proliferating Osteoblasts (HOb), fetal: Actively growing, dividing cells, in medium | Size: T-25 Flask | CAT.#: 407-25f | Price: $845.00 | |
| Proliferating Osteoblasts (HOb), fetal: Actively growing, dividing cells, in medium | Size: T-75 Flask | CAT.#: 407-75f | Price: $1,035.00 | |
| Proliferating Osteoblasts (HOb), fetal: Actively growing, dividing cells, in medium | Size: 24 Well | CAT.#: 407-24Wf | Price: $1,035.00 | |
| Proliferating Osteoblasts (HOb), fetal: Actively growing, dividing cells in medium | Size: 96 Well | CAT.#: 407-96Wf | Price: $1,155.00 |
Related Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOb Basal Medium: Basal medium (contains no growth supplement). Add GS before use. | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 416-500 | Price: $93.00 | |
| HOb Differentiation Medium: Promotes cells to change from one type to another, more specialized | Size: 250 ml | CAT.#: 417D-250 | Price: $149.00 | |
| HOb Growth Medium: All-in-one ready-to-use | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 417-500 | Price: $143.00 | |
| HOb Growth Medium Kit: Basal medium & growth supplement sold together packaged separately | Size: Yields 500 ml | CAT.#: 417K-500 | Price: $155.00 | |
| HOb Growth Medium, wo FBS: Growth medium without FBS | Size: 500 ml | CAT.#: 417F-500 | Price: $155.00 | |
| HOb Growth Supplement: Added to Basal Medium to create Growth Medium | Size: 50 ml | CAT.#: 417-GS | Price: $88.00 |
Extended Family Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse BMPR2 Antibody: Mouse BMPR2 Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CP10368 | Price: $457.00 | |
| Monoclonal Bone Morphogenic Protein 4, BMP-4, Antibody: Monoclonal Bone Morphogenic Protein 4, BMP-4, Antibody | Size: 100 ul | CAT.#: CB12470 | Price: $302.00 | |
| Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (BMP-2): Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: RP1053-10 | Price: $194.00 | |
| Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (BMP-2): Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1053-100 | Price: $624.00 | |
| Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (BMP-2): Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1053-1000 | Price: $5,327.00 | |
| Human BMP-2 ELISA Kit: Human Bone Morphogenic Protein-2 ELISA Kit | Size: 96 Wells | CAT.#: CL0311 | Price: $500.00 | |
| Human BMP-4 ELISA Kit: Human Bone Morphogenic Protein-4 ELISA Kit | Size: 96 Wells | CAT.#: CL0314 | Price: $500.00 | |
| Human BMP-5 ELISA Kit: Human Bone Morphogenic Protein-5 ELISA Kit | Size: 96 Wells | CAT.#: CL0310 | Price: $500.00 | |
| Human Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF): Human Connective Tissue Growth Factor | Size: 20 ug | CAT.#: RP1060-20 | Price: $194.00 | |
| Human Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF): Human Connective Tissue Growth Factor | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1060-100 | Price: $484.00 | |
| Human Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF): Human Connective Tissue Growth Factor | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1060-1000 | Price: $4,090.00 | |
| Osteoblast RNA (HOb RNA), Adult: Total RNA prepared from Human Osteoblasts, adult | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: 406-R10a | Price: $514.00 | |
| Osteoblast RNA (HOb RNA), Adult: Total RNA prepared from Human Osteoblasts, adult | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: 406-R25a | Price: $1,028.00 | |
| Osteoblast RNA (HOb RNA), Fetal: Total RNA prepared from Human Osteoblasts, fetal | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: 406-R10f | Price: $398.00 | |
| Osteoblast RNA (HOb RNA), Fetal: Total RNA prepared from Human Osteoblasts, fetal | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: 406-R25f | Price: $796.00 | |
| Osteoblast RNA (HOb RNA), Re-Differentiated, Fetal: Total RNA prepared from Human Osteoblasts, Differentiated, fetal | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: 406D-R10f | Price: $465.00 | |
| Osteoblast RNA (HOb RNA), Re-Differentiated, Fetal: Total RNA prepared from Human Osteoblasts, Differentiated, fetal | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: 406D-R25f | Price: $930.00 | |
| Osteoblast RNA (HOb RNA), Stimulated, Adult: Total RNA prepared from Human Osteoblasts, Stimulated, adult | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: 406S-R10a | Price: $465.00 | |
| Osteoblast RNA (HOb RNA), Stimulated, Fetal: Total RNA prepared from Human Osteoblasts, Stimulated, fetal | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: 406S-R10f | Price: $514.00 | |
| Osteoblast RNA (HOb RNA), Stimulated, Fetal: Total RNA prepared from Human Osteoblasts, Stimulated, fetal | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: 406S-R25f | Price: $1,028.00 | |
| Osteoblast RNA (HOb RNA), Stimulated, Adult: Total RNA prepared from Human Osteoblasts, Stimulated, adult | Size: 25 ug | CAT.#: 406S-R25a | Price: $930.00 | |
| Human Soluble Receptor Activator of NF-kB Ligand (RANK-Ligand): Human soluble Receptor Activator of NFκB Ligand | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: RP1019-10 | Price: $194.00 | |
| Human Soluble Receptor Activator of NF-kB Ligand (RANK-Ligand): Human soluble Receptor Activator of NFκB Ligand | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1019-100 | Price: $624.00 | |
| Human Soluble Receptor Activator of NF-kB Ligand (RANK-Ligand): Human soluble Receptor Activator of NFκB Ligand | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1019-1000 | Price: $5,327.00 | |
| Subculture Reagent Kit: 100 ml each of HBSS, Trypsin/EDTA & Trypsin Neutralizing Solution | Size: 1 Kit | CAT.#: 090K | Price: $69.00 | |
| Human RANK-Ligand, Animal-Free: Human Soluble Receptor Activator of NFκB Ligand, Animal-Free | Size: 10 ug | CAT.#: RP1019AF-10 | Price: $213.00 | |
| Human RANK-Ligand, Animal-Free: Human Soluble Receptor Activator of NFκB Ligand, Animal-Free | Size: 100 ug | CAT.#: RP1019AF-100 | Price: $687.00 | |
| Human RANK-Ligand, Animal-Free: Human Soluble Receptor Activator of NFκB Ligand, Animal-Free | Size: 1000 ug | CAT.#: RP1019AF-1000 | Price: $5,860.00 |
Resources/Documents
Citations
Publications
2017
Canal, C., Fontelo, R., Hamouda, I., Guillem-Marti, J., Cvelbar, U. and Ginebra, M.P., 2017. Plasma-induced selectivity in bone cancer cells death. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.05.023
Tarade, D., D. Ma, C. Pignanelli, F. Mansour, D. Simard, S. van den Berg, J. Gauld, J. MNulty and S. Pandey. 2017. Structurally simplified biphenyl combretastatin A4 derivatives retain in vitro anti-cancer activity dependent on mitotic arrest. PLoS ONE 12(3): e0171806.
Varley, M., A. Markaki and R. Brooks. 2017. Effect of Rotation on Scaffold Motion and Cell Growth in Rotating Bioreactors.Tiss Eng, DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2016.0357.
2016
Bellayr, I., R. Marklein, J. Lo Surdo, S. Bauer and R. Puri. 2016. Identification of Predictive Gene Markers for Multipotent Stromal Cell Bellayr, I., R. Marklein, J. Lo Surdo, S. Bauer and R. Puri. 2016. Identification of Predictive Gene Markers for Multipotent Stromal Cell Proliferation. Stem Cells & Dev, 25:861-873.
Correia, T., D. Figueira, K. de Sá, S. Miguel, R. Fradique, A. Mendonça and I.Correia.2016. 3D printed scaffolds with bactericidal activity aimed for bone tissue regeneration. Intl J Biol Macromol, 93:1432-1445.
Fradique, R., T. Correia, S. Miguel, K. de Sá, D. Figueira, A. Mendonça and I. Correia. 2016. Production of new 3D scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration by rapid prototyping. J Mater Sci: Mater Med, 27:69.
Junkar, I., M. Kulkarni, B. Drašlerc, N. Rugelj, A. Mazare, A. Flaškerb, D. Drobne, P. Humpoličeke, M. Resnik, P. Schmuki, M. Mozetiča and A. Igličb. Influence of various sterilization procedures on TiO2 nanotubes used for biomedical devices. Bioelectrochemistry, 109:79-86
Kim, G., O. Elnabawi, D. Shin and E. Pae. 2016. Transient Intermittent Hypoxia Exposure Disrupts Neonatal Bone Strength. Frontiers in Pediatrics, 4:1-9.
Ma, D. 2016. Exploiting Cancer Cell Mitochondria as Therapeutic Strategy: Structure Activity Relationship Analysis of Synthetic Analogues of Pancratistatin. PhD Dissertation, University of Windsor.
Stevenson, G., S. Rehman, E. Draper, E. Hernández-Nava, J. Hunt and J. Haycock. 2016. Combining 3D human in vitro methods for a 3Rs evaluation of novel titanium surfaces in orthopaedic applications. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 7:1586-1599.
Ueda, M., T. Goto, K. Kuroishi, K. Gunjigake, E. Ikeda, S. Kataoka, M. Nakatomi, T. Toyono, Y. Seta, and T. Kawamoto. 2016. Asporin in compressed periodontal ligament cells inhibits bone formation. Archives of Oral Biology, 62:86-92.
Ueda, M., K. Kuroishi, K. Gunjigake, E. Ikeda and T. Kawamoto. 2016. Expression of SOST/sclerostin in compressed periodontal ligament cells. Journal of Dental Sciences, 11:272-278.
Wu, R., W. Wang, G. Huang, X. Mao, Y. Chen, Q. Tang and L. Liao. 2016. Endothelin‑1 induces oncostatin M expression in osteoarthritis osteoblasts by trans‑activating the oncostatin M gene promoter via Ets‑1. Molecular Medicine Reports, 13:3559-3566.
2015
Lee, M. 2015. Use of uraria in promoting osteogenesis or providing neuroprotection. Patent US 9044476 B2.
Padilla, S., A. de Castro, A. Gar Garzón-Gutiérrez, L. Benito, S. Enciso, M. Canillas, and R. Carrodeguas. 2015. Novel Nanostructured Zn-substituted Monetite Based Biomaterial for Bone Regeneration. J Nanomed Nanotechnol, 2015, 6:5, http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000325.
Lynch, P. E. Thompson, K. McGinnis, Y. Rovira Gonzalez, J. Surdo, S. Bauer and D. Hursh. 2015. Chromatin Changes at the PPAR-γ2 Promoter During Bone Marrow-Derived Multipotent Stromal Cell Culture Correlate With Loss of Gene Activation Potential. Stem Cells, 33:2169-2181.
2014
Both, J., O. Krijgsman, J. Bras, G. Schaap, F. Baas, B. Ylstra, and T. Hulsebos. 2014. Focal Chromosomal Copy Number Aberrations Identify CMTM8 and GPR177 as New Candidate Driver Genes in Osteosarcoma. PLoS ONE 9(12): e115835.
Frandsen, C., K. Brammer, K. Noh, G. Johnston, and Sungho Jin. 2014. Tantalum coating on TiO 2 nanotubes induces superior rate of matrix mineralization and osteofunctionality in human osteoblasts. Materials Science and Engineering, 37:332–341.
Lee, Y., H. Ji, S. Lee, S. Hong, H Yang, M. Yoo1 and K. Kim. 2014. The role of adiponectin in the production of IL-6, IL-8, VEGF and MMPs in human endothelial cells and osteoblasts: implications for arthritic joints. Experimental & Molecular Medicine 46, online 17 January, e72.
Mao, Y.-W., R.-D. Lin, H.-C. Hung, and M.-H. Lee. 2014. Stimulation of Osteogenic Activity in Human Osteoblast Cells by Edible Uraria crinita. J Agric Food Chem, 62:5581–5588.
Pilia, M., T. Guda, B. Pollot, V. Aguera, and M. Appleford. 2014. Local microarchitecture affects mechanical properties of deposited extracellular matrix for osteonal regeneration. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 35:122-133.hanical properties of deposited extracellular matrix for osteonal regeneration. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 35:122-133.
2013
Kwak, J.-H., S.-R. Lee, H.-J. Park, H.-E. Byun, E.-H. Sohn, B.-O. Kim, D.-K. Rhee, and S. Pyo. 2013. Kobophenol A enhances proliferation of human osteoblast-like cells with activation of the p38 pathway. Int. Immunopharm. 17:704-713.
Pilia, M., T. Guda, B. Pollot, V. Aguero, and M. Appleford. 2013a. Local microarchitecture affects mechanical properties of deposited extracellular matrix for osteonal regeneration. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 35:122-133.
Pilia, M., T. Guda, S.M. Shiels, and M.R. Appleford. 2013b. Influence of substrate curvature on osteoblast orientation and extracellular matrix deposition. Journal of biological engineering. 7:23.
2012
Appleford, M. and M. Pilia. 2012. Cortical bone scaffold for guided osteon regeneration in load-bearing orthopaedic applications. Patent Application US 20140236312 A1.
Both, J., T. Wu, J. Bras, G.R. Schaap, F. Baas, and T.J. Hulsebos. 2012. Identification of Novel Candidate Oncogenes in Chromosome Region 17p11. 2-p12 in Human Osteosarcoma. PloS one. 7:e30907.
Frandsen, C. 2012. An Extensive Analysis of Modified Nanotube Surfaces for Next-Generation Orthopedic Implants. PhD Dissertation, UCSD.
Ni, J., C.J. Frandsen, K. Noh, G.W. Johnston, G. He, T. Tang, and S. Jin. 2012. Fabrication of thin film TiO2 nanotube arrays on Co-28Cr-6Mo alloy by anodization. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 33:1460–1466.
Shiels, S.M., K.D. Solomon, M. Pilia, M.R. Appleford, and J.L. Ong. 2012. BMP‐2 tethered hydroxyapatite for bone tissue regeneration: Coating chemistry and osteoblast attachment. J. Biomedical Materials Res. Part A. 100:3117-3123.
Shimizu, H., H. Nakagami, N. Yasumasa, O.K. Mariana, M. Kyutoku, H. Koriyama, F. Nakagami, M. Shimamura, H. Rakugi, and R. Morishita. 2012. Links Between Hypertension and Osteoporosis: Benidipine Ameliorates Osteoporosis in Ovariectomized Hypertensive Rats Through Promotion of Osteoblast Proliferation and Inhibition of Osteoclast Differentiation. Current Cardiovascular Risk Reports. 6:274-280.
Valente, J., V. Gaspar, B. Antunes, P. Countinho, and I. Correia. 2012. Microencapsulated Chitosan-Dextran Sulfate Nanoparticles For Controled Delivery Of Bioactive Molecules And Cells In Bone Regeneration. Polymer. 54:5-15.
2011
Chen, F., X. Zhang, S. Sun, J.N. Zara, X. Zou, R. Chiu, C.T. Culiat, K. Ting, and C. Soo. 2011. NELL-1, an osteoinductive factor, is a direct transcriptional target of Osterix. PloS one. 6:e24638.
Ma, D., P. Tremblay, K. Mahngar, J. Collins, T. Hudlicky, and S. Pandey. 2011. Selective cytotoxicity against human osteosarcoma cells by a novel synthetic C-1 analogue of 7-deoxypancratistatin is potentiated by curcumin. PloS one. 6:e28780.
Medici, D., and B. Olsen. 2011. Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells. Patent Application US 20130078718 A1.
Zhang, X., C. Li, H. Gao, H. Nabeka, T. Shimokawa, H. Wakisaka, S. Matsuda, and N. Kobayashi. 2011. Rho kinase inhibitors stimulate the migration of human cultured osteoblastic cells by regulating actomyosin activity. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 16:279-295.
2010
Zhang, X., A. Kovtun, C. Mendoza-Palomares, M. Oulad-Abdelghani, F. Fioretti, S. Rinckenbach, D. Mainard, M. Epple, and N. Benkirane-Jessel. 2010. SiRNA-loaded multi-shell nanoparticles incorporated into a multilayered film as a reservoir for gene silencing. Biomaterials. 31:6013-6018.
2008
Nathan, S.S., A.G. Huvos, J.E. Casas‐Ganem, R. Yang, I. Linkov, R. Sowers, G.R. DiResta, R. Gorlick, and J.H. Healey. 2008. Tumor interstitial fluid pressure may regulate angiogenic factors in osteosarcoma. J. Orthop. Res. 26:1520-1525.
Shimizu, H., H. Nakagami, M.K. Osako, R. Hanayama, Y. Kunugiza, T. Kizawa, T. Tomita, H. Yoshikawa, T. Ogihara, and R. Morishita. 2008. Angiotensin II accelerates osteoporosis by activating osteoclasts. The FASEB J. 22:2465-2475.
2004
Binnerts, M.E., X. Wen, K. Canté-Barrett, J. Bright, H.-T. Chen, V. Asundi, P. Sattari, T. Tang, B. Boyle, and W. Funk. 2004. Human Crossveinless-2 is a novel inhibitor of bone morphogenetic proteins. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 315:272-280.
2002
Gutwein, L., and T. Webster. 2002. Osteoblast and Chrondrocyte Proliferation in the Presence of Alumina And Titania Nanoparticles. Journal of Nanoparticle Research. 4:231-238.
Kay, S., A. Thapa, K.M. Haberstroh, and T.J. Webster. 2002. Nanostructured polymer/nanophase ceramic composites enhance osteoblast and chondrocyte adhesion. Tissue engineering. 8:753-761.