Product Sheet CL0494
Description
BACKGROUND RANTES (short for “regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted”) also called CCL5, belongs to the CC chemokine family and induces leukocyte migration by binding to specific receptors in the G protein–coupled receptor family. RANTES (CCL5) has been shown in vitro to mediate eosinophil, lymphocyte, neutrophil, and monocyte chemotaxis, and it initiates several other proinflammatory events, such as integrin activation, lipid mediator biosynthesis, and degranulation. RANTES production, which is generated predominantly after cellular activation in CD8+ T cells, monocytes, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and platelets. RANTES has been shown to modulate cytokine production, inducing a switch from Th2-type to Th1-type cytokines. RANTES also induces the upregulation of Th1 cytokines (IL-2 and IFN-γ) and Th2 cytokines (IL-5).1 RANTES triggers two signalling pathways in T cells. At nanomolar concentrations, G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)-mediated signal is generated, leading to cell migration. At higher concentrations (micromolar and above), a protein tyrosine kinase (PTK)-mediated signal is triggered, leading to cell activation.2 RANTES-induced activation appears not to be confined to T cells, but dual signalling pathways may also be induced in monocytes and neutrophils. A particular characteristic of RANTES is its ability to self-aggregate, forming multimers at high concentration. that the aggregation of RANTES is necessary for its activating effects. One of its receptors, CCR5, is a co-receptor for HIV entry into CD4+ cells. Together with the other chemokines which bind to CCR5, RANTES is able to suppress HIV-1 infection in vitro. In addition, high concentrations of RANTES have been shown to enhance HIV infection in vitro, independently of its binding to chemokine receptors. The enhancement of HIV infection mediated by RANTES is partially due to its activating effect on cells.3 In addition to binding specific chemokine receptors, RANTES is also able to bind to cell surface glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) which promote RANTES oligomerization): this mechanism is involved in RANTES-mediated enhancement of HIV infection.4
REFERENCES
1. Schall, T.J.: Cytokine. 3:165-83, 1991
2. Appay, V. et al: Int. Immunol. 12:1773-82, 2000
3. Appay, V. & Rowland-Jones, S.L.: Trends Immunol. 22:83-7, 2001
4. Proudfoot, A.E.I. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 276:10620-6, 2001
2. Appay, V. et al: Int. Immunol. 12:1773-82, 2000
3. Appay, V. & Rowland-Jones, S.L.: Trends Immunol. 22:83-7, 2001
4. Proudfoot, A.E.I. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 276:10620-6, 2001
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
Cat.No.: | CL0494 |
Target Protein Species: | Human |
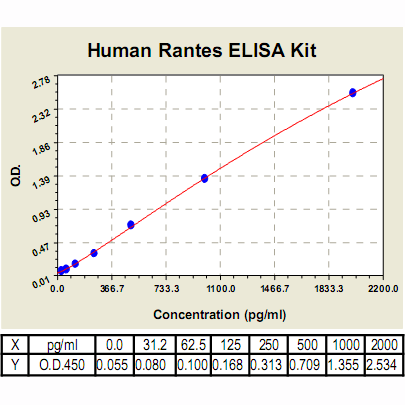
Range: | 31.2pg/ml – 2000pg/ml |
Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokine |
Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |
ELISA Kits are based on standard sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology. Freshly prepared standards, samples, and solutions are recommended for best results.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Rantes ELISA Kit: Human Regulated Upon Activation, Normal T Cell Expressed and Secreted ELISA Kit | Size: 96 Wells | CAT.#: CL0494 | Price: $500.00 |