CL0849
Description
BACKGROUND Trk (Neurotrophin) receptors are single transmembrane catalytic receptors with intracellular tyrosine kinase activity. Trk receptors are coupled to the Ras, Cdc42/Rac/RhoG, MAPK, PI 3-K and PLCgamma signaling pathways. There are four members of the Trk family; TrkA, TrkB and TrkC and a related p75NTR receptor. p75NTR lacks tyrosine kinase activity and signals via NF-kappaB activation. Each family member binds different neurotrophins with varying affinities. TrkA potently binds nerve growth factor (NGF) and is involved in differentiation and survival of neurons and in control of gene expression of enzymes involved in neurotransmitter synthesis. TrkB has highest affinity for brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and is involved in neuronal plasticity, long term potentiation and apoptosis of CNS neurons. TrkC is activated by neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and is found on proprioceptive sensory neurons. p75NTR binds neurotrophin precursors with high affinity and retains low affinity to the mature cleaved forms. TrkA was originally identified as an oncogene as it is commonly mutated in cancers, particularly colon and thyroid carcinomas.1
TrkB, while binding its high affinity ligand brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), will play an essential role for nervous system development, neuronal survival, differentiation, and maintenance. Ligand binding to TrkB receptor causes receptor dimerization and the activation of the intrinsic tyrosine kinase domain of TrkB. The initial substrate of the TrkB kinase is the receptor itself, which results from tyrosine phosphorylation of the other subunit of TrkB dimer. A tyrosine-phosphorylated TrkB recruits, phosphorylates, and activates a variety of adapter molecules that initiate downstream signaling cascades. Phosphotyrosine residues of activated TrkB-receptors serve as specific recognition sites for effector molecules that contain a Src homology 2 domain. Among the proteins that interact with tyrosine-phosphorylated TrkB are the enzymes phospholipase Cgamma (PLCgamma) and phosphoinositol 3-kinase and the adapter protein Shc. Each of these molecules activates distinct signaling pathways that may have different functions. The Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway initiated by Shc or PLCgamma is involved in cell proliferation and differentiation, while the phosphoinositol 3-kinase pathway is important for survival.2
Furthermore, accumulating evidences implies that TrkB signal pathway may also be involved in a variety of human cancers, in which TrkB is likely to play a role in initiation and metastasis of carcinomas. Overexpression of TrkB is often correlated with the tumorigenesis, angiogenesis and drug resistance in these malignancies, contributing significantly to the metastasis and aggressive phenotype of these poor prognosis tumors. The evidences to show the significant contribution of TrkB to malignancy not only came from solid tumors such as neoblastoma, pancreas cancer, Wilm\'s tumor and hepatocarcinoma, but also came from haematological malignancies such as Hodgkin lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Emerging data have suggested that TrkB may be a mediator as well as a marker of carcinogenesis and metastasis, therefore TrkB may be used as a valuable target for cancer therapy especially for the metastatic tumors with poor prognosis. The fact that TrkB is a receptor tyrosine kinase in principle allows various ways of targeted interference. Indeed, attempts are being made already to develop inhibitors of Trk kinase signaling. Preclinical xenograft studies suggest that such inhibitors can delay tumor growth.3
TrkB, while binding its high affinity ligand brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), will play an essential role for nervous system development, neuronal survival, differentiation, and maintenance. Ligand binding to TrkB receptor causes receptor dimerization and the activation of the intrinsic tyrosine kinase domain of TrkB. The initial substrate of the TrkB kinase is the receptor itself, which results from tyrosine phosphorylation of the other subunit of TrkB dimer. A tyrosine-phosphorylated TrkB recruits, phosphorylates, and activates a variety of adapter molecules that initiate downstream signaling cascades. Phosphotyrosine residues of activated TrkB-receptors serve as specific recognition sites for effector molecules that contain a Src homology 2 domain. Among the proteins that interact with tyrosine-phosphorylated TrkB are the enzymes phospholipase Cgamma (PLCgamma) and phosphoinositol 3-kinase and the adapter protein Shc. Each of these molecules activates distinct signaling pathways that may have different functions. The Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway initiated by Shc or PLCgamma is involved in cell proliferation and differentiation, while the phosphoinositol 3-kinase pathway is important for survival.2
Furthermore, accumulating evidences implies that TrkB signal pathway may also be involved in a variety of human cancers, in which TrkB is likely to play a role in initiation and metastasis of carcinomas. Overexpression of TrkB is often correlated with the tumorigenesis, angiogenesis and drug resistance in these malignancies, contributing significantly to the metastasis and aggressive phenotype of these poor prognosis tumors. The evidences to show the significant contribution of TrkB to malignancy not only came from solid tumors such as neoblastoma, pancreas cancer, Wilm\'s tumor and hepatocarcinoma, but also came from haematological malignancies such as Hodgkin lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Emerging data have suggested that TrkB may be a mediator as well as a marker of carcinogenesis and metastasis, therefore TrkB may be used as a valuable target for cancer therapy especially for the metastatic tumors with poor prognosis. The fact that TrkB is a receptor tyrosine kinase in principle allows various ways of targeted interference. Indeed, attempts are being made already to develop inhibitors of Trk kinase signaling. Preclinical xenograft studies suggest that such inhibitors can delay tumor growth.3
REFERENCES
1. Lamballe, F. et al: Cell 66:967-979, 1991
2. Guiton, M. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 270: 20384-90, 1995
3. Desmet, C.J.& Peeper, D.S.: Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:755-9, 2006
2. Guiton, M. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 270: 20384-90, 1995
3. Desmet, C.J.& Peeper, D.S.: Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:755-9, 2006
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
Cat.No.: | CL0849 |
Target Protein Species: | Human |
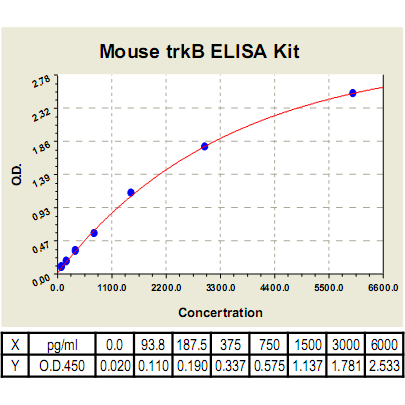
Range: | 93.8pg/ml-6000pg/ml |
Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokine. |
Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |
ELISA Kits are based on standard sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology. Freshly prepared standards, samples, and solutions are recommended for best results.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse TrkB ELISA Kit: Mouse Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase B ELISA Kit | Size: 96 Wells | CAT.#: CL0849 | Price: $511.00 |