Product Sheet CL0642
Description
BACKGROUND Thrombospondins (TSPs) are a family of homotrimeric multidomain glycoproteins that on the cellular level modulate adhesion, proliferation, and migration and have been implicated clinically in the development of atherosclerosis, angiogenesis, and oncogenesis. While initially identified in platelet alpha-granules, TSPs are also secreted by a variety of cells, including endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, astrocytes, keratinocytes, macrophages, and melanoma cells. The family of TSPs consists of five members (TSP1, -2, -3, -4, and -5) encoded by distinct genes that demonstrate a high degree of sequence homology with platelet TSP (TSP1). TSP1 and -2 form one subgroup of trimeric proteins with a role that is likely distinct from that of the pentameric TSP3, -4, and -5 subgroup.1
TSP2 is expressed in many tissues during embryonic development, in the healthy adult and in various tumor stromal environments. Predominant expression is found in the connective tissue compartment and expression is highest in bone. TSP2 expression has been reported in some tumors. TSP2 expression is upregulated by Rac1-induced reactive oxygen species, Hox A5, ACTH, TGF-beta, cerivastatin and in-vitro, by increasing cell confluency. Downregulation of TSP2 expression occurs by inhibiting TGFb-dependent p38 MAPK pathway or perturbing the Smad pathway by dexamethasone, ATF3 overexpression, human papilloma virus positive cells, cytomegalovirus infected cells, tissue factor overexpressing sarcoma cells. The oncogene c-myb affects TSP 2 expression via a post-transcriptional regulation of its mRNA stability.
TSP2 binds to extracellular matrix ligands including, TGF-beta-1, histidine rich glycoprotein, TSG6, heparin, MMP-2, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. TSP2 binds to cell surface receptors including CD36, CD47, LDL receptor-related protein-1 (via calreticulin) and the integrins alpha-V/beta-3, alpha-4/beta-1, and alpha-6/beta-1. In contrast to TSP1, TSP2 does not activate latent TGF-beta-1 but similarly to TSP1, TSP2 contains EGF-like modules that bind calcium in a cooperative manner. Moreover, it was demonstrated that TSP2 enhances Notch signaling and binds to both Jagged1 and Notch3 ectodomains, potentially bridging two essential extracellular components of Notch signaling. This process requires the participation of low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1), a TSP2 receptor. LRP1 and TSP2 stimulate Notch activity by driving trans-endocytosis of the Notch ectodomain into the signal-sending cell.2 TSP2 in a context-dependent and cell-specific manner stimulates or inhibits cell adhesion, proliferation, motility, and survival. TSP2 is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis mediated by the TSP2 receptor CD36. However, its N-terminal region exhibits pro-angiogenic activities mediated by beta-1 integrins . By way of alpha-4/beta-1, TSP2, like TSP1, modulates T cell behavior in-vitro. TSP2 stimulates chemotaxis, MMP gene expression, and activation-dependent adhesion of T cells. In a model of rheumatoid synovium, cell-based TSP2 therapy had an anti-inflammatory role in-vivo and depleted the tissue of infiltrating T cells. In the CNS, TSP2 secreted by astrocytes promotes synaptogenesis. Moreover, TSP2 also inhibits proliferation and enhances osteoblastogenesis of multipotent mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPC). Osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis are reciprocally regulated. It was shown that TSP2 significantly inhibits adipogenesis.3
TSP2 is expressed in many tissues during embryonic development, in the healthy adult and in various tumor stromal environments. Predominant expression is found in the connective tissue compartment and expression is highest in bone. TSP2 expression has been reported in some tumors. TSP2 expression is upregulated by Rac1-induced reactive oxygen species, Hox A5, ACTH, TGF-beta, cerivastatin and in-vitro, by increasing cell confluency. Downregulation of TSP2 expression occurs by inhibiting TGFb-dependent p38 MAPK pathway or perturbing the Smad pathway by dexamethasone, ATF3 overexpression, human papilloma virus positive cells, cytomegalovirus infected cells, tissue factor overexpressing sarcoma cells. The oncogene c-myb affects TSP 2 expression via a post-transcriptional regulation of its mRNA stability.
TSP2 binds to extracellular matrix ligands including, TGF-beta-1, histidine rich glycoprotein, TSG6, heparin, MMP-2, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. TSP2 binds to cell surface receptors including CD36, CD47, LDL receptor-related protein-1 (via calreticulin) and the integrins alpha-V/beta-3, alpha-4/beta-1, and alpha-6/beta-1. In contrast to TSP1, TSP2 does not activate latent TGF-beta-1 but similarly to TSP1, TSP2 contains EGF-like modules that bind calcium in a cooperative manner. Moreover, it was demonstrated that TSP2 enhances Notch signaling and binds to both Jagged1 and Notch3 ectodomains, potentially bridging two essential extracellular components of Notch signaling. This process requires the participation of low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1), a TSP2 receptor. LRP1 and TSP2 stimulate Notch activity by driving trans-endocytosis of the Notch ectodomain into the signal-sending cell.2 TSP2 in a context-dependent and cell-specific manner stimulates or inhibits cell adhesion, proliferation, motility, and survival. TSP2 is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis mediated by the TSP2 receptor CD36. However, its N-terminal region exhibits pro-angiogenic activities mediated by beta-1 integrins . By way of alpha-4/beta-1, TSP2, like TSP1, modulates T cell behavior in-vitro. TSP2 stimulates chemotaxis, MMP gene expression, and activation-dependent adhesion of T cells. In a model of rheumatoid synovium, cell-based TSP2 therapy had an anti-inflammatory role in-vivo and depleted the tissue of infiltrating T cells. In the CNS, TSP2 secreted by astrocytes promotes synaptogenesis. Moreover, TSP2 also inhibits proliferation and enhances osteoblastogenesis of multipotent mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPC). Osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis are reciprocally regulated. It was shown that TSP2 significantly inhibits adipogenesis.3
REFERENCES
1. Armstrong, L.C. & Bornstein, P.: Matrix Biol. 22:63-71, 2003
2. Meng, H. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 285:23047-55, 2010
3. Shitaye, H.S. et al: Matrix Boil. 29:549-56, 2010
2. Meng, H. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 285:23047-55, 2010
3. Shitaye, H.S. et al: Matrix Boil. 29:549-56, 2010
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Details
Cat.No.: | CL0642 |
Target Protein Species: | Human |
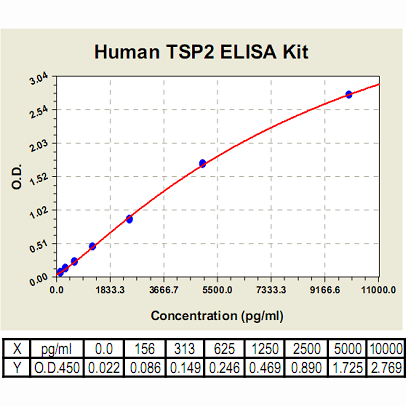
Range: | 156pg/ml-10,000pg/ml |
Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokine. |
Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |
ELISA Kits are based on standard sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology. Freshly prepared standards, samples, and solutions are recommended for best results.
Products
| Product | Size | CAT.# | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human TSP2 ELISA Kit: Human Thrombospondin 2 ELISA Kit | Size: 96 Wells | CAT.#: CL0642 | Price: $533.00 |